In this article, you’ll discover the fascinating world of insect vision and how it plays a crucial role in the field of pest control. Understanding how insects see their surroundings is key to developing effective strategies for managing and preventing pest infestations. We’ll explore the unique characteristics of insect vision, such as their ability to detect movement and perceive ultraviolet light, and how this knowledge can inform targeted pest control solutions. By the end of this article, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for the science behind insect vision and its impact on maintaining pest-free environments. So, let’s delve into the world of insects and their remarkable visual capabilities!
Insect Vision: An Overview
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on insect vision and its implications for pest control. Insects have evolved incredibly diverse visual systems that allow them to perceive and interact with their environment in unique ways. Understanding how insects see the world can provide valuable insights for developing effective pest control strategies. In this article, we will explore the structure of insect eyes, different types of insect vision, the benefits of insect vision for survival, and how this knowledge can be applied to pest control.
The Structure of Insect Eyes
Insect eyes are fascinating structures that differ significantly from human eyes. While humans have a single pair of compound eyes, insects often have multiple pairs of compound eyes and sometimes simple eyes, known as ocelli.
Compound eyes are composed of thousands of tiny units called ommatidia. Each ommatidium acts as a separate visual receptor, capturing light from a small portion of the insect’s visual field. This mosaic-like arrangement allows insects to have a wide field of view, excellent motion detection, and rapid detection of changes in light intensity.
Types of Insect Vision
Insects exhibit a range of visual capabilities that are important for their survival. One type of insect vision is color perception. While humans have three types of color receptor cells, insects often have different combinations or types of receptors, enabling them to perceive a broader spectrum of colors. Some insects can even see ultraviolet light, which is invisible to the human eye.
Another crucial aspect of insect vision is their ability to detect motion and visually track objects. This visual acuity enables them to react quickly to potential threats or prey. Insects also have the remarkable ability to detect polarized light, which aids in navigation and orientation.
Benefits of Insect Vision for Survival
Insect vision plays a vital role in their survival and reproductive success. First and foremost, color perception allows insects to recognize and differentiate between various objects in their environment, such as flowers, ripening fruits, or potential predators. This helps them identify food sources, mates, and potential dangers.
Motion detection and visual tracking are crucial for insects that rely on swift and precise movements to catch prey or escape from predators. By quickly detecting and tracking motion, insects can effectively evade predators and capture their prey.
In addition, polarized light detection provides insects with a navigational compass. Many insects, such as bees, can perceive the polarization patterns of sunlight and use this information to navigate accurately, even on cloudy days or in dense forests.
Lastly, ultraviolet vision grants insects a unique perspective on the world. Many flowers have ultraviolet markings that are invisible to humans but are highly attractive to insects. This enables insects to locate nectar-rich flowers easily, increasing their chances of successful foraging and pollination.
Visual Perception of Insects
Understanding how insects perceive the world visually can give us valuable insights into their behavior and help develop effective pest control strategies. Let’s explore the different aspects of insect visual perception in more detail.
Color Perception in Insects
While humans perceive color using three primary color receptors (red, green, and blue), insects have different combinations or types of receptors that allow them to perceive a broader spectrum of colors. Some insects, like bees and butterflies, can even detect ultraviolet light, which plays a crucial role in their foraging and reproductive behaviors.
The ability of insects to perceive and distinguish colors is heavily influenced by their unique visual system. By understanding the specific colors that attract pests or repel them, we can develop targeted pest control strategies.
Motion Detection and Visual Tracking
Insects have exceptional motion detection abilities, thanks to their compound eyes’ structure. Each ommatidium in their compound eyes acts as a separate visual receptor, allowing them to detect even subtle changes in motion. This enables insects to quickly respond to potential threats or prey, enhancing their chances of survival.
By studying how insects visually track moving objects, we can develop visual lures and traps to attract and capture pests effectively. These traps can exploit the pests’ natural instinct to follow moving targets, leading to more efficient pest control.
Polarized Light Detection
Insects possess the remarkable ability to detect polarized light. Polarized light occurs when light waves vibrate in a specific orientation. Many insects, including bees and ants, use this polarized light as a navigational aid. By perceiving the polarization patterns produced in the sky by sunlight, insects can determine their position and orientation, even in complex environments.
To leverage this knowledge for pest control, researchers are exploring the use of polarized light as a lure or trap. By replicating the polarized light patterns that attract pests, we can develop strategies that lead them away from specific areas or into traps.
Ultraviolet Vision in Insects
Ultraviolet (UV) vision is another extraordinary visual capability of insects. Many flowers have evolved to exhibit UV markings that are highly attractive to pollinators such as bees and butterflies. By detecting these UV patterns, insects can locate nectar-rich flowers more efficiently, increasing their foraging success and aiding in pollination.
For pest control purposes, understanding how pests are attracted to UV light can help us develop targeted traps or repellant devices. By manipulating UV light sources, we can either lure pests away or disrupt their ability to find suitable breeding or feeding grounds.

Implications for Pest Control
The understanding of insect vision can provide novel strategies for pest control. By targeting specific aspects of insect vision, we can develop pest control methods that are more effective and environmentally friendly. Let’s explore some of these implications in more detail.
Understanding Insect Behavior
By understanding how insects perceive their environment visually, we can gain insights into their behavior. This knowledge helps us identify the factors that attract pests to certain areas or food sources. Understanding their behavior also allows us to predict their movement patterns and develop strategies to intercept or disrupt them.
Targeting Pest Attractants
Visual attractants play a significant role in pest behavior. By identifying and manipulating these attractants, we can create strategies that lure pests away from desired areas or trap them in controlled environments. For example, by understanding the visual cues that attract mosquitoes, we can develop traps that imitate these cues, improving mosquito control measures.
Developing Visual Attractants
Building on the understanding of insect vision, researchers can develop visual attractants that specifically target pests. For example, specific colors or patterns may attract certain pests more effectively. By exploiting these preferences, we can create visual attractants that draw pests away from crops or human habitats, resulting in reduced pest populations.
The Role of Light in Pest Control
Light plays a crucial role in pest control, as insects often exhibit positive phototaxis (attraction to light) or negative phototaxis (avoidance of light). By understanding how light influences insect behavior, we can utilize it as a tool for pest monitoring and control.
Light traps, such as UV traps or pheromone traps, use light to attract and capture pests. These traps can be highly effective in monitoring and reducing pest populations. Additionally, manipulating light sources in pest-prone areas can disrupt insect circadian rhythms, disturbing their behavior and reducing their impact on crops or human habitats.
The Role of Color Perception
Insect color preferences can provide valuable insights for pest control strategies. By analyzing the colors that attract or repel pests, we can develop targeted interventions to manage their populations effectively.
Analysis of Insect Color Preferences
Researchers have conducted numerous studies to determine insects’ color preferences and how different colors influence their behaviors. For example, certain colors may repel pests, while others may attract them. By understanding these preferences, we can design traps or bait stations that exploit these visual cues, effectively managing pest populations.
Using Color for Pest Monitoring
Color-based traps and baits have proven to be highly effective in pest monitoring. By selecting colors that are attractive to specific pests and combining them with other attractants or pheromones, we can more accurately monitor pest populations. This information helps us make informed decisions about pest management interventions, reducing the reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides.
Color-Based Traps and Baits
Incorporating specific colors into traps or baits can significantly enhance their efficacy. For instance, yellow or blue sticky traps are commonly used to capture flying pests like aphids or whiteflies. These traps exploit the pests’ attraction to certain colors, luring them onto the sticky surface for control.

Motion Detection and Visual Tracking
The ability to detect motion and visually track objects is essential for insects’ survival. By understanding how insects respond to visual cues and develop strategies to exploit their motion detection abilities, we can enhance pest control methods.
The Importance of Movement
Insects are highly sensitive to motion and often use it as a primary cue for identifying prey, avoiding predators, or locating resources. By incorporating motion into pest control strategies, we can create visually enticing lures or traps that effectively attract and capture pests.
Using Visual Lures and Traps
Visual lures and traps that incorporate movement can be powerful tools for pest control. By imitating the movements of prey or potential mates, we can attract pests into controlled environments where they can be monitored or eliminated. These traps take advantage of the pests’ natural instincts to react to moving objects, increasing the effectiveness of pest control measures.
Behavioral Disruption Techniques
In addition to exploiting motion detection for lures and traps, researchers also explore behavioral disruption techniques. By disrupting the insects’ normal behavioral patterns through the use of moving lights or other visual interventions, we can reduce their ability to locate food sources or mate, resulting in decreased pest populations.
Polarized Light Detection
Insects have a unique ability to detect and utilize polarized light. By understanding how insects perceive polarized light and its significance for their behavior, we can design pest control strategies that take advantage of this knowledge.
Insects’ Ability to Detect Polarized Light
Many insects, including bees, ants, and dragonflies, have specialized eyes that can detect the polarization patterns of sunlight. This ability aids in their navigation and orientation, allowing them to maintain a sense of direction even when landmarks are not visible.
Utilizing Polarized Light as a Pest Control Approach
The use of polarized light in pest control is still an emerging field of research. However, researchers are exploring the potential of replicating polarized light patterns that attract pests and using them as lures or traps. By manipulating polarized light sources, we may be able to manipulate the movement patterns of pests or lead them away from sensitive areas, such as crops or residential areas.
Ultraviolet Vision in Insects
Ultraviolet (UV) vision provides insects with a unique perspective on the world. By understanding how insects utilize UV light and incorporating this knowledge into pest control strategies, we can enhance our ability to manage pests efficiently.
The Unique Ultraviolet Perspective
Many flowers have evolved to exhibit UV markings that are highly attractive to pollinators like bees and butterflies. By perceiving these UV patterns, insects can efficiently locate nectar-rich flowers, aiding in their foraging success and contributing to pollination. Understanding this unique perspective helps us develop targeted interventions to manipulate insect behaviors.
Leveraging UV Light for Pest Management
Leveraging UV light for pest management involves using specific UV wavelengths or patterns to attract, trap, or repel pests. For example, UV light traps can effectively capture various flying pests, such as mosquitoes or moths, reducing their populations and the associated risks. Incorporating UV-reflective surfaces into pest control devices can also disrupt the pests’ ability to locate suitable habitats or food sources, reducing their impact.
Understanding Insect Behavior
To effectively control pests, it is crucial to understand the factors that influence their behavior. Visual cues play a significant role in insect navigation, feeding, and reproduction, and by understanding these cues, we can develop targeted pest control strategies.
Factors Influencing Insect Behavior
Insect behavior is influenced by a combination of factors, including visual cues, pheromones, temperature, humidity, and host plant characteristics. Visual cues, in particular, strongly affect their foraging behavior, mate selection, and orientation. By identifying and manipulating these factors, we can create interventions that disrupt their behaviors and reduce their impact.
Visual Cues for Navigation and Feeding
Insects rely on visual cues to navigate their environment and locate food sources. By understanding which visual cues attract pests or guide them to their preferred habitats, we can develop interventions that modify or manipulate these cues. For example, altering the visual landscape through the use of repellent plants or objects can deter pests from entering specific areas.
Effect of Light on Insect Circadian Rhythms
Light plays a vital role in regulating the circadian rhythms of insects. By manipulating the light environment, we can disrupt their normal behaviors and reduce their ability to reproduce or locate suitable habitats. For instance, utilizing light traps or introducing artificial light sources can interfere with the mating or feeding behaviors of pests, effectively reducing their populations.
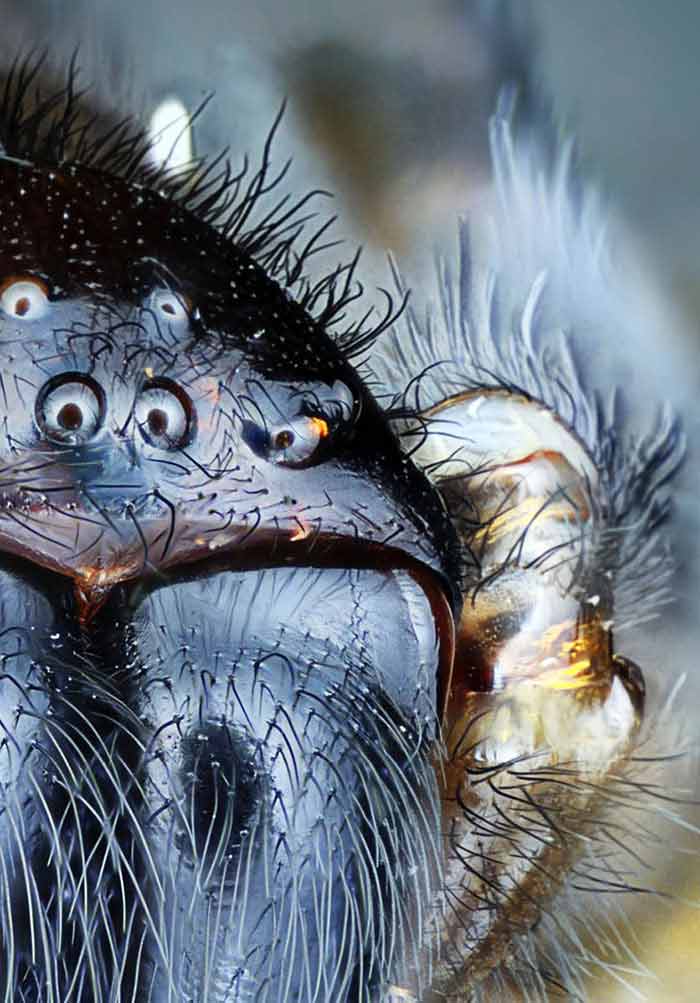

Targeting Pest Attractants
Understanding the visual attractants that lure pests into specific areas allows us to develop targeted pest control strategies that disrupt their behavior or trap them effectively.
Visual Attractants in Pest Management
Visual attractants can play a significant role in pest management by luring pests away from desired areas or into controlled environments. By identifying the specific visual cues that attract pests, we can develop interventions that exploit these cues. For example, designing traps or baits that incorporate colors or patterns attractive to specific pests can lead to more efficient pest control.
Identifying and Manipulating Attractant Sources
Identifying the attractant sources that draw pests to certain areas is essential in managing pest populations. By eliminating or manipulating these sources, we can create environments that are less attractive to pests. For instance, proper waste management can reduce the availability of food sources for pests, decreasing their population size and minimizing potential infestations.
Using Visual Decoys and Repellents
Visual decoys and repellents can be effective tools for pest control. Decoys, such as visual lures that mimic the appearance of desired targets, can divert pests away from important areas. Repellents that exploit specific visual cues can deter pests from entering specific habitats or crops, reducing their impact and the need for chemical interventions.
The Role of Light in Pest Control
Light plays a critical role in pest control, as insects exhibit different phototactic behaviors (attraction or avoidance of light). By understanding how light influences insect behavior, we can utilize it to monitor and control pest populations.
Effect of Light on Insect Behavior
Light can have diverse effects on insect behavior, depending on the species and their natural behaviors. Some insects are positively phototactic, meaning they are attracted to light sources, while others are negatively phototactic, actively avoiding light. By manipulating light sources, we can influence insect behavior and their likelihood of entering specific areas.
Using Light Traps for Pest Monitoring
Light traps are commonly used for monitoring and capturing flying pests, such as moths or mosquitoes. These traps replicate the appearance of favorable habitats or prey, attracting pests towards the light source. Monitoring with light traps provides valuable data on pest populations, allowing for timely interventions and accurate pest control measures.
Light-Based Pest Control Strategies
Light-based pest control strategies involve manipulating the light environment to disrupt or deter pests. For example, using specific light wavelengths or intensities can interfere with pests’ circadian rhythms, reducing their reproduction or feeding behaviors. Incorporating artificial light sources in pest-prone areas can also create unfavorable conditions, deterring pests from entering or colonizing those areas.
By harnessing the knowledge of insect vision and its implications for pest control, we can develop more effective and sustainable strategies to manage pest populations. Understanding how insects perceive their environment visually allows us to target specific aspects of their vision, such as color perception, motion detection, polarized light detection, and ultraviolet vision.
Building on this understanding, researchers and pest control professionals can develop strategies that exploit these visual cues to lure pests away from desired areas, disrupt their behaviors, or trap them effectively. By adopting these targeted and environmentally friendly approaches, we can minimize the reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides and create more sustainable pest control solutions.

I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.