In the world of pest control, there is a crucial player that often goes unnoticed: the government. While many may not realize it, the government plays a significant role in regulating pest control practices to ensure the safety and well-being of both humans and the environment. From setting standards and protocols to enforcing laws and licensing requirements, the government works tirelessly to maintain a balance between effective pest control and the protection of public health. Join us as we explore the vital role of government in overseeing pest control practices and the impact it has on our everyday lives.
1. Introduction to Pest Control Practices
1.1 Definition and Importance of Pest Control
Pest control refers to the management and elimination of pests that can cause harm or damage to humans, animals, crops, and the environment. It involves the use of various techniques and methods to prevent, control, and eradicate pests. The importance of pest control cannot be overstated as pests can transmit diseases, destroy crops, damage property, and adversely impact public health. Effective pest control practices are necessary to ensure a safe and healthy environment for all.
1.2 Common Types of Pests
There are various types of pests that can be found in different environments. Common pests include insects such as mosquitoes, flies, ants, bed bugs, and cockroaches. Other pests can include rodents like rats and mice, termites, birds, and wildlife. Each type of pest requires specific control measures to effectively manage their populations and minimize their negative impact on human health and ecosystems.
2. Overview of Government Regulation
2.1 Purpose of Government Regulation
Government regulation plays a crucial role in pest control practices to protect public health, preserve the environment, and ensure the effectiveness and safety of pest control products and methods. The purpose of government regulation is to establish standards, guidelines, and laws that govern the use, application, and distribution of pest control products. It aims to reduce the risks associated with the use of pesticides, promote the use of environmentally friendly methods, and maintain the quality and safety standards in the pest control industry.
2.2 Agencies Responsible for Regulation
In most countries, government agencies are responsible for regulating pest control practices. These agencies include the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the United Kingdom, and the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA) in Australia. These agencies are tasked with the oversight and enforcement of regulations related to pest control products, their labels, and the licensing requirements for professionals in the industry.
2.3 Laws and Regulations
Government regulation of pest control practices is enforced through laws and regulations. These laws and regulations specify the requirements for pesticide registration, labeling, storage, handling, application, and disposal. They also outline the obligations of pest control professionals, including certification and licensing requirements. Additionally, regulations may establish restrictions on certain chemicals or methods to protect public health, non-target species, and ecosystems.
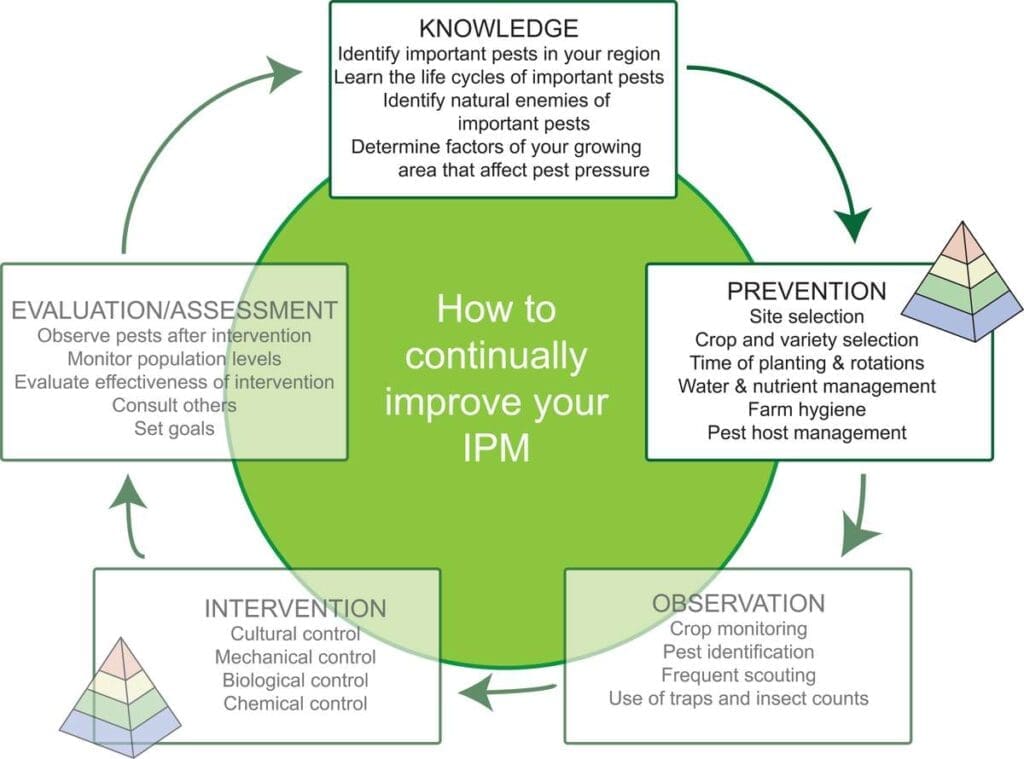
3. Protecting Public Health
3.1 Controlling Disease Vectors
One of the primary objectives of pest control practices is to control disease vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks, that transmit harmful diseases to humans and animals. Government regulation ensures that effective measures are in place to control and manage these pests. This includes the use of targeted insecticides, habitat modification, and public awareness campaigns to reduce the risk of vector-borne diseases. By controlling disease vectors, the government plays a vital role in safeguarding public health and preventing disease outbreaks.
3.2 Minimizing Exposure to Harmful Chemicals
While pest control is essential, it is equally important to minimize the exposure of humans, animals, and the environment to potentially harmful chemicals used in pest control practices. Government regulation enforces strict guidelines and safety standards to ensure that pest control products are used responsibly and safely. This includes evaluating the toxicity of chemicals, setting maximum residue limits, and providing guidelines on proper use, personal protective equipment, and restricted areas. By minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals, the government helps protect the health and well-being of both individuals and ecosystems.
4. Environmental Considerations
4.1 Impact on Non-Target Species
Pest control practices have the potential to impact non-target species, such as beneficial insects, birds, and mammals. Government regulation emphasizes the importance of minimizing harm to non-target species through the implementation of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies. IPM focuses on using a combination of techniques, such as biological control, cultural practices, and targeted pesticide use, to manage pests effectively while minimizing the impact on non-target species. This approach helps maintain the delicate ecological balance and preserve biodiversity.
4.2 Preservation of Ecosystems
Ecosystem preservation is a significant concern in pest control practices, as the indiscriminate use of pesticides can have adverse effects on ecosystems. Government regulation promotes the use of environmentally friendly pest control methods and encourages the preservation of natural habitats. By implementing regulations that restrict or ban the use of certain chemicals, the government helps prevent harm to ecosystems, including water bodies, soil, and vegetation. This ensures the long-term sustainability and health of ecosystems and the organisms that depend on them.

5. Quality and Safety Standards
5.1 Certification and Licensing Requirements
Government regulation establishes certification and licensing requirements for pest control professionals to ensure their competence in handling and applying pest control products. By obtaining these certifications, professionals demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of safety protocols, proper product use, and potential risks. This helps maintain a high level of expertise and professionalism within the industry and ensures that pest control services are delivered safely and effectively.
5.2 Labeling and Use Instructions
To ensure the safe and proper use of pest control products, government regulation requires accurate labeling and use instructions to be provided on product packaging. These labels provide important information about the product, including active ingredients, precautions, application rates, and safety guidelines. By enforcing strict labeling regulations, the government enables users to make informed decisions and use pest control products responsibly. This helps prevent misuse, reduce accidents, and maintain safety standards.
6. Enforcement and Inspections
6.1 Inspection Procedures
Government agencies responsible for regulating pest control practices conduct regular inspections to ensure compliance with laws and regulations. Inspection procedures may involve visits to pest control companies, storage facilities, and application sites. During inspections, agencies check for adherence to safety protocols, proper use of products, record-keeping practices, and compliance with licensing requirements. These inspections help identify any violations and facilitate the enforcement of regulations to maintain industry standards.
6.2 Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with government regulations can have serious consequences. Penalties for violations of pest control regulations may include fines, suspension or revocation of licenses, and legal action. By imposing penalties for non-compliance, government agencies maintain the integrity of pest control practices, protect public health, and deter unethical and unsafe practices within the industry. The enforcement of regulations acts as a deterrent and encourages pest control professionals to adhere to standards and guidelines.

7. Role of Research and Development
7.1 Funding Research Initiatives
Government agencies play a vital role in funding research initiatives related to pest control practices. Research helps identify new and innovative methods, develop safer and more effective pest control products, and improve existing techniques. By funding research initiatives, the government contributes to the advancement of pest control practices and ensures that industry professionals have access to the latest scientific knowledge and technology.
7.2 Promoting Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that focuses on prevention, monitoring, and using a combination of techniques to manage pests effectively. Government regulation promotes the use of IPM strategies and encourages the integration of biological controls, cultural practices, and chemical interventions to minimize pesticide use and environmental impact. By promoting IPM, the government fosters sustainable pest control practices and reduces reliance on chemical pesticides.
8. International Cooperation and Standards
8.1 Harmonization of Regulations
Pests and pest control practices do not recognize national borders. To address this challenge, international cooperation and the harmonization of regulations are essential. Government agencies collaborate with international organizations and participating countries to develop harmonized standards and regulations for pest control practices. This fosters consistency, facilitates trade, and ensures that pest control products meet uniform safety and quality standards across borders.
8.2 Sharing Best Practices
Government agencies also play a role in sharing best practices and lessons learned with other countries and organizations. Through international conferences, workshops, and collaborations, governments exchange information, knowledge, and experiences related to pest control practices. This knowledge-sharing helps improve pest control strategies, enhances safety measures, and promotes innovative approaches to managing pests. By sharing best practices, governments contribute to the global development and advancement of pest control practices.

9. Economic Impact and Cost Analysis
9.1 Effects on Pest Control Industry
Government regulation can have both positive and negative effects on the pest control industry. On one hand, regulation ensures the safety and quality of pest control practices, which enhances the reputation and credibility of the industry. It also creates a level playing field, as all professionals must meet the same standards and comply with regulations. On the other hand, regulation can impose additional costs on businesses, particularly in terms of compliance, licensing, and training requirements. However, the economic impact of regulation must be weighed against the benefits of protecting public health, preserving the environment, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of pest control practices.
9.2 Cost-Benefit Analysis of Regulations
Government agencies are responsible for conducting cost-benefit analyses of regulations to assess their economic impact and justify their implementation. Cost-benefit analysis involves evaluating the costs associated with compliance, enforcement, and other regulatory measures, as well as quantifying the benefits in terms of health and environmental protection. This analysis helps policymakers make informed decisions, strike a balance between regulation and economic considerations, and ensure that regulations are effective and justified.
10. Challenges and Future Directions
10.1 Addressing Resistance and Pesticide Usage
One of the significant challenges in pest control practices is the development of resistance in pests to commonly used pesticides. This challenge requires ongoing research and the development of innovative pest control methods. Government agencies must collaborate with industry professionals and researchers to address resistance and reduce reliance on chemical pesticides. Integrated pest management, biological controls, and the development of new non-chemical approaches can help overcome this challenge.
10.2 Adapting to Emerging Threats
As the global environment changes, new pest threats emerge, requiring proactive and adaptive pest control strategies. Government regulation must be flexible and responsive to these emerging threats, allowing for the timely implementation of effective control measures. This includes investing in research and development, promoting the use of sustainable pest control practices, and fostering partnerships between government agencies, industry professionals, and researchers. By adapting to emerging threats, governments can ensure the continued effectiveness and safety of pest control practices.
In conclusion, government regulation plays a crucial role in the effective and safe implementation of pest control practices. Through the establishment of standards, enforcement of regulations, and promotion of research and development, governments protect public health, preserve ecosystems, and maintain the quality and safety standards in the pest control industry. While challenges exist, international cooperation, the sharing of best practices, and the adaptation to emerging threats can help foster sustainable pest control practices for the future.

I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.