Are you looking for natural and effective pest control solutions? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the fascinating role that birds play in pest control. Birds are not only beautiful and majestic creatures, but they also serve as valuable allies in keeping pest populations in check. From insect-eating birds that feast on pesky mosquitoes and flies to seed-eating birds that prevent crops from being destroyed by pests, these winged wonders are nature’s own pest controllers. Join us as we delve into the world of avian pest control and discover how birds can be your secret weapon in maintaining a pest-free environment.
1. Introduction
1.1 Importance of pest control in agriculture
Pest control plays a vital role in agriculture, as it helps protect crops from the damaging effects of pests. These pests can include insects, rodents, and even birds. Without effective pest control measures, agricultural yields can be significantly reduced, leading to food shortages and economic losses. Therefore, it is essential to explore all possible avenues of pest control, including the role of birds in this process.
1.2 Role of birds in pest control
While birds may not be the first creatures that come to mind when considering pest control, they actually play a significant role in regulating pest populations in agricultural settings. Many bird species feed on insects, rodents, and other pests that can cause substantial damage to crops. These birds act as natural predators, helping to maintain a balance in the ecosystem and reducing the reliance on chemical pesticides. In this article, we will delve into the types of pest birds, their behaviors, and the impact of their predation on pest populations.
2. Types of Pest Birds
2.1 Common pest bird species
Several bird species are known to cause concerns in agricultural areas due to their pest-like behavior. These include the European Starling, House Sparrow, Pigeon, and Crow. These birds tend to congregate in large numbers and can cause significant damage to crops through feeding and nest building activities.
2.2 Characteristics of pest birds
Pest birds often possess certain characteristics that make them particularly troublesome for farmers. They can adapt well to a variety of environments, are highly intelligent, and can quickly learn to exploit available food sources. Additionally, some pest birds are known to be aggressive and compete with native bird species for resources.
2.3 Bird behaviors that aid in pest control
One of the reasons why birds are effective in pest control is their foraging behaviors. Many pest bird species actively search for insects, rodents, and other pests in agricultural fields, devouring them as a food source. They are skilled hunters and can cover large areas in search of prey. Birds also help in pest control through their keystone species role, which we will discuss further in the subsequent sections.
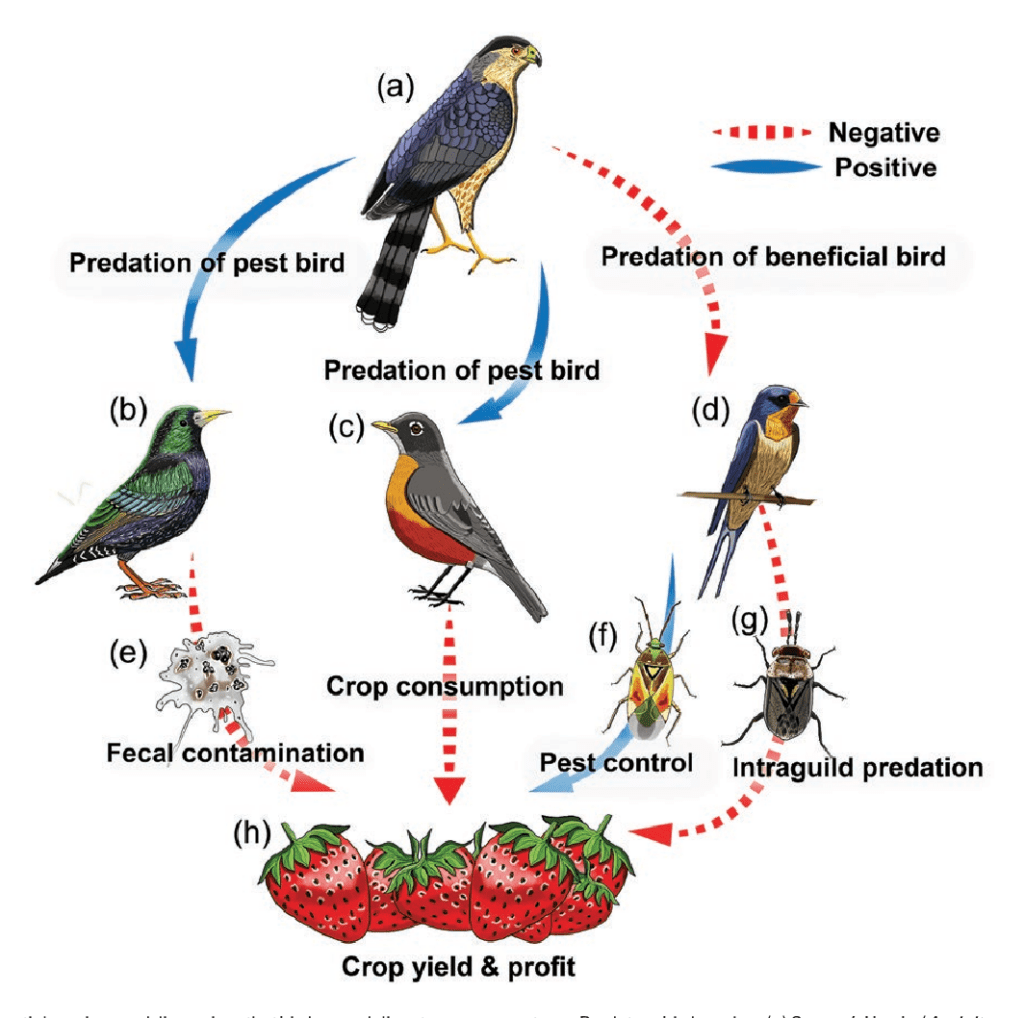
3. Bird Predation on Agricultural Pests
3.1 Birds as natural predators
Birds have evolved over thousands of years to adapt to their environments, and part of this adaptation includes the development of predatory behaviors. In agricultural settings, birds act as natural predators by preying on insects, rodents, and other pest species. They help control pest populations by consuming large numbers of these pests, effectively reducing their impact on crops.
3.2 Examples of pests targeted by birds
Birds target a wide variety of pests that can cause significant damage to agricultural crops. Some commonly targeted pests include caterpillars, grasshoppers, aphids, and mice. These pests can devastate crops if left unchecked, leading to decreased yields and economic losses for farmers. In such instances, the predatory nature of birds becomes crucial in maintaining crop health.
3.3 Impact of bird predation on pest populations
The predation of pests by birds can have a significant impact on pest populations. By actively consuming pests, birds help control their numbers and prevent outbreaks that can lead to crop damage. This natural form of pest control not only reduces the need for chemical pesticides but also helps maintain a balance within the ecosystem. The presence of birds in agricultural landscapes can promote sustainable pest management practices and contribute to the overall health of the environment.
4. Ecosystem Services Provided by Birds
4.1 Bird pollination and seed dispersal
Birds provide essential ecosystem services beyond pest control. Many bird species act as pollinators, aiding in the reproduction of flowering plants. Through their feeding behaviors, birds transfer pollen from one flower to another, facilitating plant fertilization and fruit production. Some birds also play a vital role in seed dispersal by consuming fruits and later excreting the undigested seeds in different locations, aiding in the expansion and diversity of plant populations.
4.2 Nutrient cycling through bird droppings
Bird droppings, or guano, are rich in nutrients that can fertilize the soil. When birds feed on insects and other prey, they release fecal matter that contains valuable nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This nutrient cycling through bird droppings helps replenish the soil’s fertility, promoting healthy plant growth. Consequently, the presence of birds in agricultural areas can have a positive impact on soil quality and overall crop productivity.
4.3 Pest control as a part of overall ecosystem services
While the focus of this article is on bird-based pest control, it is essential to acknowledge the broader range of ecosystem services that birds provide. By contributing to pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling, birds play a multifaceted role in maintaining the overall health and functioning of ecosystems. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these services is crucial for adopting holistic and sustainable approaches to pest management in agriculture.

5. Strategies for Attracting Pest Control Birds
5.1 Providing suitable bird habitats
To attract pest control birds to agricultural areas, it is essential to create suitable habitats that meet their specific needs. This can be achieved by incorporating native plant species into the landscape, as they provide food sources and nesting sites for birds. Maintaining a diverse range of vegetation types, including trees, shrubs, and grasses, will attract a variety of bird species and promote their presence as natural pest control agents.
5.2 Food sources to attract pest control birds
Offering a reliable source of food is an effective way to attract pest control birds to agricultural areas. Planting flowering plants that produce nectar and attract insects can provide a natural food source for birds such as hummingbirds. Additionally, strategically placing bird feeders stocked with appropriate bird feed can help supplement their diet, encouraging them to remain in the vicinity and target pests.
5.3 Nesting sites and shelter for birds
Providing nesting opportunities and shelter for birds is crucial in attracting them to agricultural landscapes. Birds require suitable nesting sites, such as birdhouses, tree cavities, or dense shrubbery, to raise their young. By including these features in agricultural areas, farmers can create an inviting environment for pest control birds to establish breeding populations. Additionally, the presence of sheltered areas, such as hedgerows or windbreaks, can offer protection from predators and adverse weather conditions.
6. Conservation and Protection of Pest Control Birds
6.1 Importance of protecting bird populations
Protecting bird populations is not only essential for the preservation of biodiversity but is also directly linked to sustainable pest management in agriculture. When bird populations decline due to habitat loss or other threats, the natural pest control they provide diminishes, leading to an increased reliance on chemical pesticides. To maintain a healthy balance within agricultural ecosystems, it is crucial to conserve and protect the populations of pest control birds.
6.2 Threats to pest control bird populations
Several threats can negatively impact the populations of pest control birds. Habitat loss and degradation due to agricultural intensification, urbanization, and deforestation are primary concerns. Additionally, pesticide use without proper precautions can directly harm birds and disrupt their reproductive success. Climate change, pollution, and invasive species also pose significant threats to bird populations and their ability to contribute to pest control.
6.3 Conservation efforts and best practices
Efforts to conserve and protect pest control birds involve a combination of individual actions and collective initiatives. Farmers can contribute by implementing bird-friendly agricultural practices, such as creating habitat corridors, minimizing pesticide use, and preserving natural vegetation. Conservation organizations and government agencies play a vital role in implementing policies and programs that prioritize bird conservation and promote sustainable agriculture. By working together, we can ensure the long-term viability of both pest control birds and agricultural productivity.

7. Scare Tactics for Pest Bird Control
7.1 Visual deterrents to discourage pest birds
Visual deterrents can be effective in deterring pest birds from agricultural areas. Installing objects such as scarecrows, reflective tape, or balloons with realistic predator eyes can create a visual disturbance that birds perceive as a threat. By using these visual deterrents, farmers can disrupt bird feeding patterns and discourage them from causing damage to crops.
7.2 Auditory devices for bird control
Sound can be an effective tool in deterring pest birds. Auditory devices that emit high-frequency sounds, distress calls, or predator noises can create an unfavorable environment for birds and disrupt their communication and feeding behaviors. However, it is important to consider the potential impact on other bird species and wildlife, ensuring that the use of auditory devices is targeted and humane.
7.3 Physical barriers to prevent bird damage
Installing physical barriers can be an effective long-term solution to prevent bird damage in agricultural areas. Examples include netting, fencing, or bird spikes installed on ledges or rooftops. These barriers act as deterrents and prevent birds from accessing crops or infrastructure, reducing the potential for damage caused by pest birds.
8. Combining Bird Control Methods with other Pest Control Measures
8.1 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach
Integrating bird control methods with other pest control measures forms a cohesive approach known as Integrated Pest Management (IPM). IPM focuses on combining various strategies to manage pests effectively while minimizing harm to the environment and human health. By including bird-based pest control methods within an IPM framework, farmers can enhance the sustainability of their pest management practices and reduce reliance on chemical pesticides.
8.2 Role of birds in reducing chemical pesticide use
Bird-based pest control can significantly contribute to reducing the use of chemical pesticides in agriculture. By harnessing the natural predatory behavior of birds, farmers can rely on nature’s pest control services instead of solely relying on synthetic chemicals. This not only reduces the potential harm to the environment and human health but also minimizes the development of pesticide resistance in pest populations, leading to more sustainable pest management practices in the long run.
8.3 Applying bird control methods alongside other pest control techniques
Bird control methods should be viewed as complementary to other pest control techniques rather than standalone solutions. It is essential to consider the specific context and pest pressures in each agricultural setting and adopt a combination of appropriate strategies. By combining bird control methods with practices such as crop rotation, biological control agents, and cultural control measures, farmers can optimize their pest management efforts and achieve more successful outcomes.

9. Case Studies and Success Stories
9.1 Real-life examples of bird-based pest control
Real-life examples highlight the practical benefits of incorporating bird-based pest control into agricultural practices. One such example is the use of Barn Owls to control rodent populations in vineyards. By providing nesting boxes and suitable habitat, vineyard owners have successfully attracted Barn Owls, which naturally prey on vine-damaging rodents. This environmentally-friendly approach has reduced the use of chemical rodenticides and improved the overall health of the vineyard ecosystem.
9.2 Success stories from farms and agricultural practices
Success stories from farms and agricultural practices demonstrate the positive impacts of promoting bird-friendly practices. Farmers who have actively encouraged bird populations through habitat restoration and the provision of food sources have reported reduced pest damage to their crops. These success stories not only highlight the effectiveness of bird-based pest control but also serve as inspiration for others to adopt sustainable pest management practices that benefit both the environment and agricultural productivity.
10. Conclusion
10.1 Summary of the role of birds in pest control
Birds play a crucial role in pest control in agriculture through their predatory behaviors and their contribution to the overall health of ecosystems. Many bird species actively target pests that can cause significant damage to crops, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and promoting sustainable pest management practices. Additionally, birds provide essential ecosystem services such as pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling, which further enhance agricultural productivity.
10.2 Importance of promoting bird-friendly practices for sustainable pest management
To maintain the valuable role of birds in pest control, it is crucial to promote bird-friendly practices in agriculture. Creating suitable habitats, providing food sources, and protecting bird populations are key steps towards sustainable pest management. By adopting integrated approaches that combine bird control methods with other pest control measures, farmers can achieve effective pest management while minimizing environmental impacts. Encouraging the conservation of pest control birds not only benefits farmers but also contributes to the preservation of biodiversity, creating a win-win situation for agriculture and the environment.


I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.