In the world of pest control, the rise of organic insecticides has been a hot topic of discussion. People are increasingly concerned about the potential health and environmental hazards associated with traditional chemical insecticides, and they are searching for safer alternatives. But the question remains: are organic insecticides truly effective in combating pests? In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of organic insecticides and delve into the scientific evidence behind their claims. Whether you’re a homeowner looking for practical solutions or a curious reader interested in the latest trends, this article will provide you with valuable insights on the efficacy of organic insecticides.
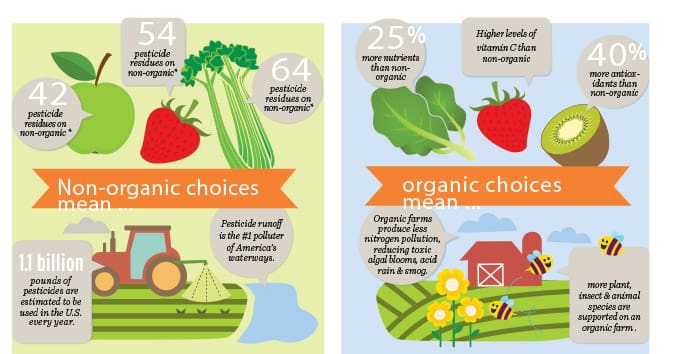
Benefits of Organic Insecticides
Reduced Environmental Impact
Organic insecticides offer a significant reduction in environmental impact compared to conventional insecticides. Conventional insecticides often contain harmful chemicals that can contaminate soil, water, and air. These chemicals can have long-lasting effects on ecosystems and can harm beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife. In contrast, organic insecticides are made from naturally occurring substances and are biodegradable, minimizing their impact on the environment.
Safe for Humans and Pets
One of the greatest benefits of organic insecticides is their safety for humans and pets. Conventional insecticides can pose health risks and may cause allergic reactions or respiratory problems. Organic insecticides, on the other hand, use natural ingredients that are less likely to cause harm to humans and pets. This makes them an ideal choice for households with children, pets, or anyone concerned about their health and well-being.
Targeted Pest Control
Organic insecticides offer targeted pest control, focusing on specific pests without harming beneficial insects or disrupting the natural balance of ecosystems. Conventional insecticides often have a broad spectrum of activity and can kill both harmful and beneficial insects. In contrast, organic insecticides are designed to target specific pests, minimizing the impact on non-target species. This targeted approach helps maintain a healthy and sustainable environment.
Different Types of Organic Insecticides
Botanical Insecticides
Botanical insecticides are derived from plants and contain natural compounds that have insecticidal properties. Examples include pyrethrum, derived from chrysanthemums, and rotenone, derived from roots of various tropical plants. Botanical insecticides are effective against a wide range of pests and have a low environmental impact.
Microbial Insecticides
Microbial insecticides utilize microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses to control pests. These microorganisms infect and kill specific pests, leaving beneficial insects unharmed. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a bacterial insecticide, is commonly used to control caterpillar pests. Microbial insecticides are highly target-specific and pose minimal risk to humans and the environment.
Mineral-Based Insecticides
Mineral-based insecticides, such as diatomaceous earth and kaolin clay, work by physically disrupting pests’ outer covering and causing dehydration or suffocation. These insecticides are effective against pests like aphids, mites, and snails. They have low toxicity to humans and the environment and are often used in organic farming.
Insecticidal Soaps
Insecticidal soaps are made from fatty acids derived from plant oils or animal fats. These soaps penetrate and disrupt the insect’s cell membranes, causing dehydration and death. They are effective against soft-bodied pests like aphids, whiteflies, and mealybugs. Insecticidal soaps have a low toxicity profile, making them safe to use around humans and pets.
Neem Oil
Neem oil is derived from the seeds of the neem tree and has been used for centuries as a natural insecticide. It contains compounds that disrupt the life cycle of insects and act as a repellent. Neem oil is effective against a wide range of pests, including aphids, mites, and beetles. It is safe to use around humans, pets, and beneficial insects when used as directed.
Effectiveness of Organic Insecticides
Effectiveness Varies by Pest Type
The effectiveness of organic insecticides can vary depending on the type of pest being targeted. Some pests may be more susceptible to organic insecticides, while others may require alternative pest control methods. Understanding the specific pests you are dealing with and the most effective organic insecticide for that pest will help ensure successful pest control.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effectiveness
Organic insecticides may provide immediate control of pests, but their long-term effectiveness can depend on various factors. Continuous and proper application is crucial to maintaining control over time. Furthermore, incorporating other pest control methods, such as cultural practices and biological control, can enhance the long-term effectiveness of organic insecticides.
The Importance of Proper Application
To maximize the effectiveness of organic insecticides, proper application is essential. Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer, including the correct dilution rates and application methods. Applying the insecticide at the right time of day and under favorable weather conditions can also enhance its efficacy. Remember to reapply as necessary, especially after rain or as pests reemerge.
Challenges of Using Organic Insecticides
Limited Spectrum of Control
One of the challenges of using organic insecticides is their limited spectrum of control. While they can be highly effective against certain pests, they may not be as effective against others. Organic insecticides are often more selective in their target, which means they may not provide control for a wide range of pests. It is important to identify the specific pests you are dealing with to choose the most appropriate organic insecticide.
Lower Persistence
Compared to conventional insecticides, organic insecticides generally have lower persistence. This means they break down more quickly in the environment, requiring more frequent applications for ongoing pest control. While this may be seen as a disadvantage, the lower persistence of organic insecticides contributes to their reduced environmental impact and safety for humans and pets.
More Frequent Application
Due to their lower persistence, organic insecticides often require more frequent application than conventional insecticides. This can be a challenge for individuals who prefer a “set it and forget it” approach to pest control. However, with proper monitoring and regular application, organic insecticides can effectively manage pest populations without the need for constant application of harmful chemicals.

Considerations for Using Organic Insecticides
Integrated Pest Management Approach
An integrated pest management (IPM) approach involves combining multiple pest control methods, including organic insecticides, to achieve long-term pest control. By integrating cultural, biological, and physical controls, organic insecticides can be used more effectively and efficiently as part of an overall pest management strategy. This approach reduces reliance on any single control method and promotes sustainable pest control practices.
Understanding Pest Life Cycles
To effectively use organic insecticides, it is crucial to understand the life cycles of the pests you are targeting. Different pests have specific vulnerabilities at different stages of their life cycle. By targeting these vulnerable stages with organic insecticides, you can disrupt the pest’s life cycle and significantly reduce populations. Understanding the pest’s biology and behavior helps in timing the application and maximizing its effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Organic Insecticide
Selecting the appropriate organic insecticide for your specific pest problem is essential for achieving optimal results. Consider factors such as the pest type, severity of infestation, and environmental conditions. Research different organic insecticides and their effectiveness against your target pest to make an informed decision. It may also be helpful to consult with a pest control professional or extension service for guidance.
Tips for Maximizing Effectiveness
Apply at the Right Time
Timing is crucial when using organic insecticides. Applying the insecticide when pests are most vulnerable, such as during their active feeding or reproduction periods, can improve its effectiveness. Additionally, consider weather conditions that can influence the effectiveness of the insecticide, such as temperature and humidity. Following the recommended timing guidelines for the specific organic insecticide will help maximize its efficacy.
Follow Instructions Carefully
Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using organic insecticides. Proper dilution rates, application methods, and safety precautions are essential for achieving the desired results. Deviating from the instructions can lead to ineffective pest control or potential harm to humans, pets, or the environment. It is also important to store organic insecticides securely and dispose of any unused product according to local regulations.
Combine with Other Pest Control Methods
To enhance the effectiveness of organic insecticides, consider incorporating other pest control methods into your pest management strategy. This may include cultural practices such as removing pest habitats or using physical barriers, as well as biological controls like using beneficial insects to prey on pests. By combining different control methods, you can create a comprehensive and sustainable approach to pest management.
Managing Expectations
Realistic Expectations for Organic Insecticides
While organic insecticides can be highly effective when used correctly, it is important to have realistic expectations. They may not provide the same immediate knockdown effect as some conventional insecticides. Organic insecticides work by targeting pests over time and reducing their populations. It may take several applications to achieve desired control. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the pest control program are necessary for long-term success.
Monitoring and Adjustment
Regular monitoring is essential in managing pests and ensuring the effectiveness of organic insecticides. Monitor the pest populations and damage levels to assess the impact of the insecticide and make adjustments as necessary. If pest populations are not adequately controlled, consider adjusting the application timing, concentration, or incorporating additional control methods. By closely monitoring the effectiveness, you can make informed decisions and optimize pest control efforts.
Benefits of Organic Insecticides Over Conventional Insecticides
Reduced Chemical Exposure
Organic insecticides provide a significant benefit over conventional insecticides by reducing chemical exposure to humans, pets, and the environment. The use of natural ingredients minimizes risks associated with toxic chemicals, offering a safer alternative for pest control. By choosing organic insecticides, you can reduce chemical exposure in your home or garden and promote a healthier living environment.
Preventing Pest Resistance
Another advantage of organic insecticides is their ability to prevent pest resistance. Conventional insecticides often target pests with specific chemical compounds, leading to the development of resistance over time. Organic insecticides, on the other hand, utilize multiple modes of action that make it difficult for pests to develop resistance. By rotating between different organic insecticides and incorporating other pest control methods, you can prevent the emergence of resistant pests.

Legislation and Regulation
Certifications and Organic Standards
Organic insecticides are subject to certifications and organic standards to ensure their quality and adherence to organic principles. Look for organic certifications such as USDA Organic or Ecocert to guarantee that the insecticide meets the specific criteria for organic production. These certifications provide assurance that the insecticide is safe, environmentally friendly, and derived from natural ingredients.
Government Regulations on Organic Insecticides
Government regulations play a crucial role in the oversight and safety of organic insecticides. Regulatory agencies establish guidelines and standards to ensure that organic insecticides meet specific safety and efficacy requirements. By complying with these regulations, organic insecticides undergo rigorous testing and approval processes, providing consumers with confidence in their effectiveness and safety.
Conclusion
Organic insecticides offer numerous benefits over conventional insecticides. They provide reduced environmental impact, are safe for humans and pets, and offer targeted pest control. However, it is important to consider the specific challenges associated with organic insecticides, such as limited spectrum of control and more frequent application. By understanding pest life cycles, following proper application techniques, and integrating other pest control methods, you can maximize the effectiveness of organic insecticides. Remember to have realistic expectations, regularly monitor and adjust your pest management efforts, and consider the advantages of organic insecticides in reducing chemical exposure and preventing pest resistance. With careful consideration and proper use, organic insecticides can be an effective and environmentally friendly solution for pest control.


I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.