Living in the city versus living in the countryside comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. One aspect that often goes unnoticed is the presence of pests. In this comparative study, we will explore the varying types of pests found in urban and rural settings, shedding light on the reasons behind their prevalence, potential risks, and effective pest control solutions. Whether you are a city dweller or enjoy the tranquility of the countryside, understanding the nuances of pest infestations can help you protect your home and maintain a healthy living environment.
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive article on pests in urban vs. rural settings. Living in either of these settings comes with its own unique challenges when it comes to pest infestation. In this article, we will discuss the factors that influence pest infestation in urban and rural areas, as well as the common pests you might encounter in each setting. Additionally, we will explore the health risks associated with these pests and the pest control methods that are effective in both environments.
Definition of Urban and Rural Settings
Before we dive into the world of pests, let’s define what we mean by urban and rural settings. Urban settings are characterized by densely populated areas with a high concentration of buildings, infrastructure, and human activity. On the other hand, rural settings are typically more spread out, with lower population densities and larger tracts of undeveloped land. Understanding these distinctions is crucial as they directly impact the types and prevalence of pests in each environment.

Factors Influencing Pest Infestation
Several factors influence pest infestation in both urban and rural settings. By understanding these factors, we can gain valuable insights into why certain pests are more common in each environment and tailor our pest control methods accordingly.
Population Density
Population density plays a significant role in determining the prevalence of pests. Urban areas, with their higher population densities, provide a multitude of resources for pests to thrive, including food waste, shelter, and hiding places. Rural areas, with lower population densities, may still experience pest infestation, but to a lesser extent due to the lack of readily available resources.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation, heavily influence pest activity. Urban areas, with their heat-absorbing concrete and asphalt, tend to have warmer microclimates, attracting pests that thrive in higher temperatures. On the other hand, rural areas, surrounded by more natural environments, may experience a wider range of pests depending on the local climate and ecological factors.
Availability of Shelter and Food Sources
The availability of shelter and food sources greatly impacts pest infestation. Urban areas provide abundant shelter options for pests, such as buildings, cracks in walls, and sewers. Additionally, the presence of restaurants and food waste increases the availability of food sources. In rural areas, pests may seek shelter in barns, sheds, and other structures, while food sources can include crops, stored grains, and livestock.
Human Habits and Activities
Human habits and activities can inadvertently contribute to pest infestation. In urban areas, improper waste management and lack of sanitation can attract pests like rats, mice, and flies. Conversely, in rural areas, improper storage of food or garbage can lead to infestations of rodents, raccoons, and other pests. Understanding these behaviors can help us develop effective pest control strategies.
Common Pests in Urban Settings
Now let’s take a closer look at some of the most common pests you might encounter in urban settings. By understanding their habits and characteristics, we can better prevent and control their infestation.
Rats and Mice
Rats and mice are notorious urban pests that thrive in human habitats. They can easily find food and shelter in homes, restaurants, and commercial buildings. Besides being carriers of diseases, these rodents can cause significant property damage by gnawing through electrical wires, plastic pipes, and wooden structures.
Cockroaches
Cockroaches are resilient pests that thrive in urban environments due to the abundant food sources and warm microclimates provided by buildings. They contaminate food, trigger allergies, and are known to spread diseases such as salmonella and E. coli.
Bed Bugs
Bed bugs have experienced a resurgence in recent years and are a common nuisance in urban areas. They infest mattresses, sofas, and other furniture, causing itchy bites and sleepless nights. Bed bugs are challenging to eliminate without professional intervention.
Ants
Ants are highly adaptable pests that can invade urban spaces in search of food and water. They form colonies and can quickly overrun a kitchen or pantry if left unchecked. While most ants are simply a nuisance, certain species can deliver painful bites or cause property damage.
Flies
Flies are attracted to urban areas due to the abundance of food waste. They can quickly multiply and become a major annoyance, especially in warmer months. Flies can contaminate food and spread diseases by landing on surfaces and transferring bacteria.
Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes thrive in urban areas with stagnant water sources such as puddles, birdbaths, and improperly maintained swimming pools. They are not only irritating with their bites, but they can also transmit diseases such as dengue fever, Zika virus, and West Nile virus.
Termites
Termites are an urban pest that poses a significant threat to buildings and wooden structures. They feed on cellulose material, including wood, and can cause extensive damage if left untreated. Detection and professional treatment are essential to prevent costly repairs.
Pigeons
Pigeons are a common sight in urban areas, often roosting on buildings and creating a mess with their droppings. Besides being an aesthetic nuisance, pigeon droppings can harbor diseases and damage buildings over time.
Squirrels
Squirrels commonly inhabit urban areas, seeking shelter in attics, garages, and crawl spaces. While generally harmless, they can cause property damage by chewing through electrical wires and insulation. Proper exclusion techniques are necessary to prevent their entry.
Raccoons
Raccoons are another urban pest that can cause trouble in garbage bins, gardens, and attics. They are known for their dexterity in opening trash cans and can create a mess while searching for food. Certain raccoons may also carry diseases like rabies.
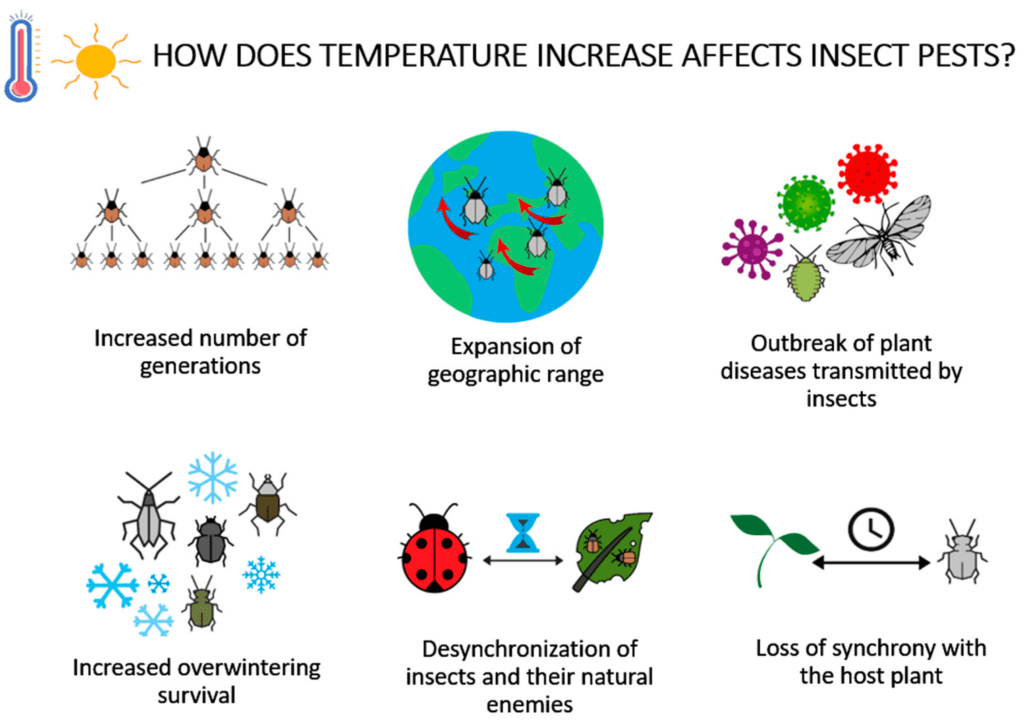
Common Pests in Rural Settings
Moving on to rural environments, let’s explore the pests that are commonly encountered in these settings. Understanding their behavior and characteristics is essential for effective pest control in agricultural and livestock-based areas.
Rodents
Rodents, such as rats and mice, are not exclusive to urban areas and can be a nuisance in rural settings as well. They can damage crops, contaminate stored grains, and carry diseases that can affect livestock and humans alike.
Ticks
Ticks are a common pest in rural areas, especially in regions with abundant vegetation. They can transmit serious diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever to humans and animals. Proper precautions, such as wearing protective clothing and using tick repellents, are crucial when venturing into tick-infested areas.
Fleas
Fleas are often associated with pets but can also infest rural areas where there are domesticated animals and wildlife. They can cause itchy bites and transmit parasites, such as tapeworms, to pets and humans. Effective flea control involves treating both pets and the environment.
Bees and Wasps
Bees and wasps play a vital role in pollination, but their presence in rural areas can lead to conflicts with humans. In some cases, their nests can pose a threat to those with allergies or can be a nuisance near outdoor dining areas. It is important to take precautions and contact professionals for safe removal when dealing with stinging insects.
Moles
Moles are pests that tunnel through lawns, gardens, and agricultural fields, causing damage to plant roots and creating unsightly mounds. Proper mole control techniques involve trapping or repelling these underground pests.
Deer
Deer can be beautiful creatures, but they can also pose challenges in rural areas where agriculture and gardens are common. They can cause extensive damage to crops, gardens, and landscapes, requiring effective deer fencing or repellents to protect valuable plants.
Coyotes
Coyotes are adaptable predators that often inhabit rural areas. While they play a crucial role in balancing ecosystems, they can pose a threat to livestock and small pets. Proper livestock management practices and secure enclosures are essential precautions against coyote predation.
Wild Boars
Wild boars, also known as feral pigs, can cause significant damage to crops, pastures, and natural areas. They are highly invasive and reproduce rapidly, making control efforts challenging. Specialized methods, such as trapping and hunting, may be required to manage wild boar populations.
Snakes
Rural areas with natural habitats are home to a variety of snake species, some of which pose no threat to humans while others are venomous. It’s important to educate yourself about the local snake species, take precautions when working outdoors, and contact professionals for snake removal if necessary.
Birds
Birds, such as pigeons and seagulls, can still be a nuisance in rural areas. They can damage crops, contaminate livestock feed, and cause property damage with their nests. Implementing effective bird control methods, such as netting or deterrents, can help minimize the impact of bird infestations.
Health Risks Associated with Urban Pests
Urban pests not only cause annoyance and property damage but also pose significant health risks to humans. Let’s explore some of the health risks associated with these pests.
Spread of Diseases
Many urban pests can carry and transmit diseases to humans. Examples include rats spreading leptospirosis and hantavirus, mosquitoes transmitting dengue fever and West Nile virus, and cockroaches causing asthma and allergies.
Allergies and Asthma
Certain pests, such as cockroaches and dust mites, can trigger allergies and asthma in sensitive individuals. Their droppings and shed skin particles can become airborne and cause respiratory distress, particularly in enclosed urban spaces.
Property Damage
Urban pests like rats, termites, and squirrels can cause significant property damage. Rats can gnaw through electrical wires, termites can destroy wooden structures, and squirrels can chew through insulation. These damages can lead to costly repairs and compromised safety.
Contamination of Food and Water
Pests like roaches, flies, and rodents can contaminate food and water sources in urban areas. The pathogens they carry can lead to food poisoning and waterborne illnesses. Proper food storage and regular pest control are essential in preventing contamination.

Health Risks Associated with Rural Pests
Rural pests also present unique health risks to humans, particularly those living in close proximity to agricultural and natural environments.
Tick-Borne Diseases
Ticks in rural areas can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and ehrlichiosis. These diseases can cause flu-like symptoms and, if left untreated, can lead to more severe complications.
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is a prevalent tick-borne illness occurring in rural areas where ticks are abundant. It can cause symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and joint pain. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term health issues.
West Nile Virus
Mosquitoes in rural areas can carry and transmit the West Nile virus to humans. Symptoms range from mild flu-like illness to severe neurological conditions. Taking precautions to prevent mosquito bites, such as using repellents and eliminating standing water, is essential in reducing the risk.
Bacterial Infections
Rural areas with livestock and wildlife can harbor bacteria that can cause infections in humans. Examples include E. coli and Salmonella, which can be transmitted through direct contact or consumption of contaminated food or water.
Venomous Bites and Stings
Venomous spiders, snakes, and stinging insects, such as bees and wasps, are hazards in rural environments. Depending on the region, encounters with these creatures can lead to painful bites or stings, and some individuals may experience severe allergic reactions that require immediate medical attention.
Pest Control Methods in Urban Settings
Controlling pests in urban settings requires a combination of preventive measures and targeted pest control methods. Let’s explore some effective pest control strategies commonly used in urban areas.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM is a holistic approach to pest control that focuses on long-term prevention and low-impact methods. It involves regular monitoring, identifying pests and their breeding sites, implementing preventive measures, and using least-toxic control methods when necessary.
Chemical Pesticides
Chemical pesticides are occasionally used in urban areas when targeted pest control is required. However, their use should be limited and only undertaken by trained professionals who understand the potential risks and adhere to safety guidelines.
Biological Control
Biological control involves using natural predators or parasites to control pest populations. For example, introducing ladybugs to control aphids or using nematodes to combat certain soil-borne pests. This method minimizes the use of chemicals and helps maintain ecological balance.
Ultrasonic Devices
Ultrasonic devices emit high-frequency sound waves that claim to repel pests such as rodents and insects. While these devices are widely available, their effectiveness is still debatable, and they may have limited success in controlling certain pests.
Exclusion Techniques
Exclusion techniques involve sealing off potential entry points to prevent pests from entering buildings. This can include sealing cracks and gaps, installing door sweeps, and using screens on windows. Proper sanitation and waste management practices also play a vital role in pest prevention.
Professional Pest Control Services
In cases of severe infestations or complex pest problems, it is recommended to seek professional pest control services. Pest control professionals have the expertise and tools to effectively identify and eliminate pests while minimizing risks to humans and the environment.
Pest Control Methods in Rural Settings
Pest control in rural settings poses unique challenges, especially when dealing with pests that affect crops, livestock, and natural habitats. Here are some effective pest control methods commonly used in rural areas.
Traps and Baits
Traps and baits are commonly used to control pests like rodents and insects in rural areas. They can be strategically placed around fields, barns, or entry points to help monitor and reduce pest populations.
Hunting and Predators
Hunting can be an effective way to control and manage certain pests in rural areas. For example, deer hunting helps regulate deer populations, reducing damage to crops and forests. Additionally, attracting natural predators, such as barn owls or beneficial insects, can help control pest populations.
Insect-Repelling Plants
Using insect-repelling plants, such as marigolds or lavender, around gardens and fields can help deter pests. These plants emit natural compounds that repel insects and act as a natural pest control method.
Crop Rotation and Companion Planting
Crop rotation and companion planting are practices used in organic farming to reduce pest pressures. By alternating crops and planting pest-repellent companion plants, farmers can disrupt pest life cycles and reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
Insect Netting and Fencing
Insect netting and fencing can be used to physically exclude pests from crops, gardens, and livestock areas. These barriers prevent pests from accessing plants or vulnerable livestock, reducing damage and the need for chemical interventions.
Livestock Management
Implementing proper livestock management practices, such as proper bedding, manure management, and rotation of grazing areas, can help prevent and control pests. Regular inspections and prompt treatment for livestock pests, such as ticks or fleas, are essential for animal health.
Challenges of Pest Control in Rural Settings
Pest control in rural settings presents its own set of challenges that differ from urban environments. Here are some key challenges to consider when implementing pest control measures in rural areas.
Vast Land Size
Rural areas often encompass large tracts of land, making effective pest control challenging. It requires additional resources and planning to cover expansive areas and mitigate pest issues efficiently.
Limited Accessibility
Some rural areas may have limited access to professional pest control services or resources. Accessibility constraints can make timely interventions difficult, potentially allowing pest populations to grow unchecked.
Variable Environmental Conditions
Rural areas often have variable environmental conditions due to diverse habitats and landscape features. Pest control efforts must adapt to these conditions, considering factors like microclimates, water sources, and neighboring ecosystems.
Wildlife Interference
Rural pest control efforts need to be mindful of the impact on wildlife populations. Harmful control methods can indirectly harm non-target species or disrupt the ecological balance of natural habitats.
Proximity to Natural Habitats
Rural areas often coexist with natural habitats, which can serve as reservoirs for pests. Close proximity to forests or wetlands can pose challenges in managing pests that migrate from these habitats into agricultural or residential areas.
In conclusion, pests are a common challenge in both urban and rural settings. While the types of pests may vary, the impact on human health and property is significant in both environments. By understanding the factors influencing pest infestation, identifying common pests, and implementing appropriate pest control methods, we can minimize the risks associated with these unwanted intruders. Whether you reside in an urban or rural area, it’s important to prioritize preventive measures, seek professional help when necessary, and maintain a clean and sanitary living environment to ensure a pest-free and healthy living space.


I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.