In the ever-changing world of climate, there is an intricate web of connections that we often overlook. One of these connections lies between pests and climate change. As temperatures shift and ecosystems evolve, pests have found new ways to thrive and survive. From the increased spread of disease-carrying mosquitoes to the invasion of crop-damaging insects, the impact of climate change on pest populations is a topic that deserves our attention. Join us on a journey as we explore the fascinating connection between pests and climate change, uncovering the ways in which our changing climate affects our encounters with these unwanted guests.
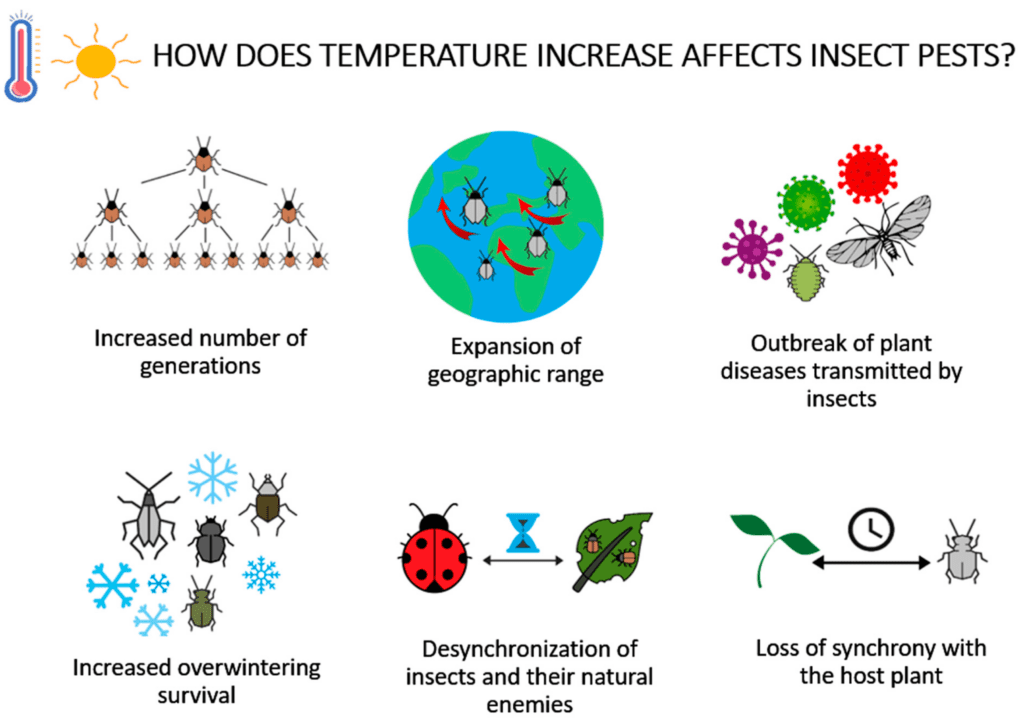
Impact of Climate Change on Pest Behavior
Changing Temperatures and Pest Activity
Climate change, with its rising temperatures, has a profound impact on the behavior of pests. As temperatures increase, pests such as insects and rodents become more active and proliferate at faster rates. Warmer temperatures speed up the reproduction and development cycles of pests, leading to increased populations and infestations. This means that pests that were previously limited by colder climates may now thrive in areas that were once unsuitable for their survival.
Shifts in Geographic Distribution
With the changing climate, many pests are shifting their geographic distribution. As temperatures rise, pests are moving to higher latitudes and elevations in search of suitable habitats. This means that areas that were previously free from certain pests may now experience infestations. For example, certain mosquito species that were once limited to tropical regions are now being found in temperate climates. This shift in distribution can have significant implications for pest control strategies and the management of new pest species.
Changes in Pest Lifecycles
Climate change can also disrupt the lifecycles of pests. Many pests, such as insects, follow seasonal patterns in their life stages, such as egg-laying, hatching, or migration. However, with the changing climate, these patterns are being disrupted. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can cause mismatches between the timing of key life events and the availability of resources. This can lead to imbalances in pest populations and challenges in predicting and managing pest outbreaks effectively.
Climate Change and Pest Control Challenges
Increased Resistance to Pesticides
One of the significant challenges posed by climate change is the increased resistance of pests to pesticides. As pests become more active and reproduce at faster rates, they are exposed to higher levels of pesticides. This increased exposure can lead to the development of resistance in pest populations over time. Additionally, warmer temperatures can also affect the effectiveness of certain pesticides, as they may degrade more quickly or evaporate before reaching their targets. This resistance and reduced efficacy of pesticides create a challenge for pest control professionals in effectively managing pest populations.
New Pest Species and Invasions
Climate change also facilitates the introduction and establishment of new pest species in different regions. As pests shift their geographic distribution, they can invade new areas where they may not have had natural predators or effective control measures. These invasive pest species can cause significant damage to crops, ecosystems, and infrastructure, as they may lack natural enemies or have adapted to withstand local conditions. The management of these new pest species requires careful monitoring, early detection, and the development of integrated pest management strategies to minimize their impact.
Altered Timing for Pest Management
With shifting pest lifecycles and unpredictable weather patterns, climate change can disrupt the timing of pest management activities. Pest control professionals rely on accurate forecasting and timing to apply control measures effectively. However, changing temperatures and weather patterns can lead to earlier or delayed pest activity, throwing off traditional management schedules. This makes it challenging for pest control professionals to plan and execute pest management strategies effectively. Adaptation and flexibility in pest management practices are essential to address these timing challenges caused by climate change.
Climate Change and Crop Pest Outbreaks
Effects on Agriculture
Climate change has significant implications for agricultural practices and crop production. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events create favorable conditions for pests to thrive. Crop pests, such as insects, mites, and weeds, can cause significant yield losses and damage to crops. Their feeding activity, accompanied by the stress caused by changing climatic conditions, weakens plants and makes them more susceptible to diseases. This puts food security at risk and increases the economic burden on farmers.
Crop Pest Species and Their Response to Climate Change
Different pest species respond differently to climate change, with some benefiting from the changing conditions and others facing challenges. Some pests, such as certain aphids and whiteflies, tend to flourish in warmer temperatures, leading to increased infestations. On the other hand, changing rainfall patterns and increased drought conditions can negatively impact pests that rely on specific moisture levels, such as soil-dwelling insects. Understanding the specific responses of crop pests to climate change is crucial in developing effective pest management strategies.
The Role of Climate in Pest Outbreaks
Climate plays a crucial role in triggering pest outbreaks. Extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, floods, and droughts, can disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems and create favorable conditions for pests to thrive. These disturbances can lead to rapid population growth and outbreaks of pests. Additionally, changing temperatures and altered climatic conditions can also affect the natural enemies of pests, such as predators and parasites, potentially reducing their effectiveness in controlling pest populations. It is essential to consider the influence of climate in predicting and mitigating pest outbreaks.
Climate Change and Urban Pest Problems
Increased Urbanization and Pest Infestations
Climate change, coupled with increased urbanization, has led to a rise in pest infestations in urban areas. As more areas are developed and natural habitats are encroached upon, pests are forced to seek alternative food, water, and shelter sources in urban environments. Additionally, urban areas often have higher temperatures and create microclimates that are conducive to pest survival. This has resulted in increased infestations of pests such as rodents, cockroaches, bed bugs, and mosquitoes in urban settings.
Effects on Human Health
The increase in urban pest infestations caused by climate change poses risks to human health. Pests like mosquitoes and ticks are vectors for various diseases, including dengue fever, Zika virus, Lyme disease, and West Nile virus. As these pests proliferate in warmer temperatures, the risk of disease transmission to humans increases. Additionally, urban pests can also cause allergic reactions and asthma exacerbations in susceptible individuals. It is essential to address urban pest problems to protect human health in the face of climate change.
Adaptation Strategies for Urban Pest Control
To combat the challenges posed by climate change on urban pest problems, adaptation strategies need to be implemented. Integrated pest management (IPM) approaches that emphasize prevention, monitoring, and targeted control strategies are crucial. This involves identifying and sealing entry points, reducing pest-friendly environments, and utilizing eco-friendly pest control measures. Public education and awareness campaigns can also play a crucial role in fostering community engagement and promoting sustainable pest control practices in urban areas.
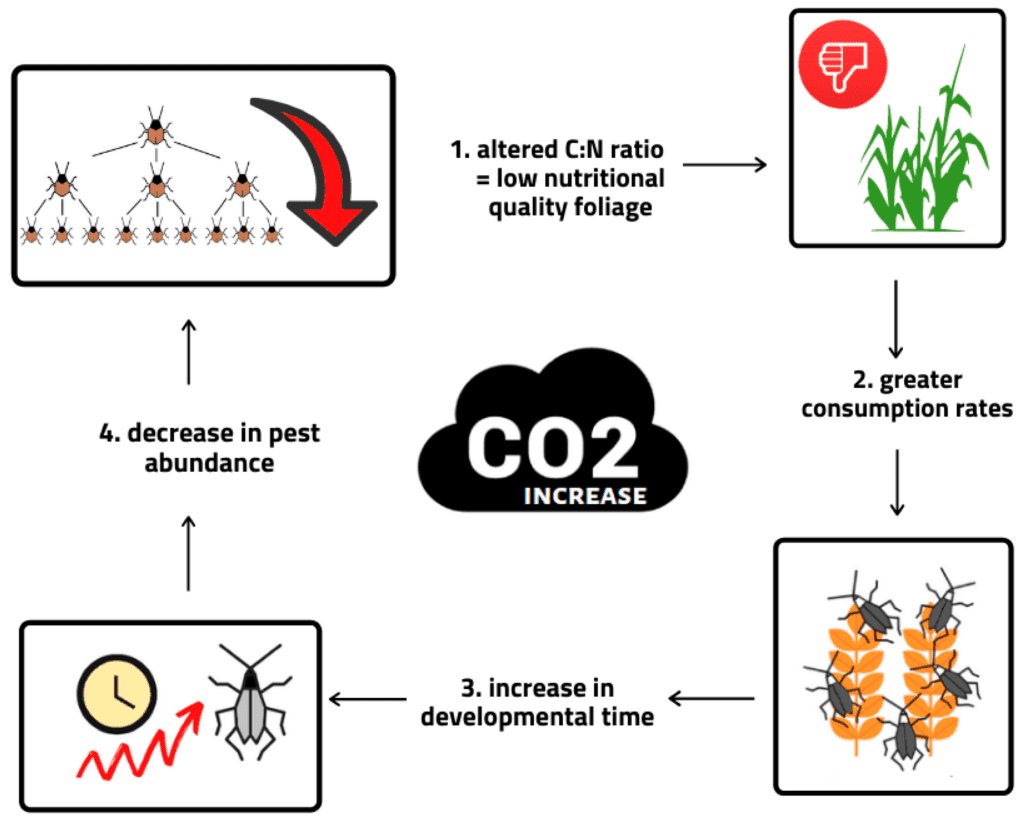
Impact of Climate Change on Disease Vector Pests
Spread of Vector-Borne Diseases
Climate change has a direct impact on the spread of vector-borne diseases through its influence on disease vector pests. Warmer temperatures can accelerate the development and reproduction of disease vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas. This can increase their population sizes and expand their geographic ranges, leading to the spread of diseases to new areas. Changes in precipitation patterns can also create breeding habitats for disease vectors, further exacerbating the transmission of diseases.
Changes in Disease Distribution and Incidence
Climate change can result in shifts in the distribution and incidence of vector-borne diseases. As disease vector pests adapt to new climatic conditions, they can move into regions previously free from certain diseases. This expansion of diseases can have significant public health implications, particularly in areas where populations may be unprepared for dealing with these diseases. Furthermore, changing climatic conditions can alter the transmission dynamics of diseases, affecting the timing and intensity of outbreaks.
Vector Control Challenges in a Changing Climate
The challenges posed by climate change to vector control are significant. Traditional vector control measures may become less effective as disease vectors adapt to changing climates. Insecticide resistance can also develop in disease vector populations due to increased exposure. Additionally, climate change can impact the availability of resources necessary for effective vector control, such as water for mosquito larvae control or suitable habitats for biological control agents. Adaptation and innovation in vector control strategies are necessary to combat the changing dynamics of vector-borne diseases.
Climate Change and Invasive Species
Impacts of Climate Change on Invasive Species
Climate change has profound impacts on invasive species, both in terms of their establishment and spread. Rising temperatures and changing climatic conditions can facilitate the success of invasive species by providing them with more favorable environments for survival and reproduction. Additionally, climate change can disrupt ecosystems and weaken native species, creating opportunities for invasive species to outcompete and dominate. These impacts can lead to the loss of biodiversity, ecosystem degradation, and economic losses.
Climate-Driven Invasions
Climate change can also drive the invasion of new areas by non-native species. As the climate becomes more favorable to certain invasive species, they can expand their range and establish populations in regions previously unsuitable for their survival. This can lead to ecological imbalances, as invasive species may lack natural enemies or control measures in their new habitats. Additionally, the introduction of invasive species can have negative impacts on native flora and fauna, disrupting ecosystem functions and services.
Control and Management Strategies for Invasive Species
Managing invasive species in the face of climate change requires a comprehensive and integrated approach. Early detection and rapid response are crucial to prevent the establishment and spread of invasive species. Control measures may include the use of targeted pesticides, biological control agents, and physical removal methods. Restoration and conservation efforts aimed at enhancing ecosystem resilience can also help prevent or mitigate the impacts of invasive species. Effective management strategies should take into account the specific ecological characteristics of invasive species and their interactions with changing climates.
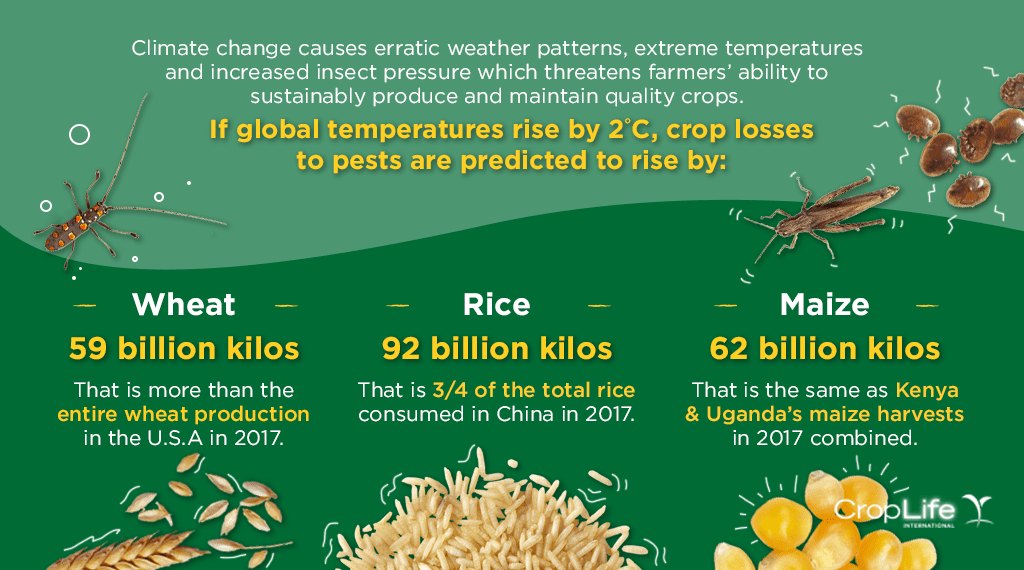
Climate Change Mitigation and Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management Strategies
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies play a vital role in mitigating the impacts of climate change on pest management. IPM focuses on using a combination of preventative, non-chemical, and targeted chemical control measures to manage pests effectively while minimizing the use of pesticides. By promoting ecosystem health, enhancing natural pest control services, and adopting sustainable agricultural practices, IPM contributes to reducing pest pressures and building resilience in the face of climate change.
Biological Control Approaches
Biological control is another important component of climate change mitigation in pest management. This approach involves the use of natural enemies, such as predators, parasites, and pathogens, to control pest populations. By harnessing the services of these natural enemies, biological control reduces reliance on pesticides and promotes ecological balance. Climate change can influence the effectiveness of biological control agents, as their efficacy may be affected by changes in temperature, precipitation, and the availability of resources. Research and innovation in biological control approaches are crucial for adapting to changing pest dynamics.
Resilient Agriculture Practices
Climate change calls for the adoption of resilient agriculture practices that can withstand and adapt to changing conditions. Practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and soil conservation contribute to building resilience in agricultural systems. By promoting soil health, enhancing water use efficiency, and conserving biodiversity, resilient agriculture practices create environments that are less prone to pest infestations and outbreaks. Additionally, these practices can contribute to mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The Role of Public Awareness and Education
Understanding Climate Change and Pest Interactions
Public awareness and education are essential for fostering understanding of the connection between climate change and pest interactions. By providing information on the impacts of climate change on pest behavior, distribution, and management, individuals can make informed decisions and take appropriate actions. Understanding the link between climate change and pests can empower homeowners, farmers, and communities to implement sustainable pest management practices and contribute to climate change mitigation efforts.
Promoting Sustainable Pest Control Practices
Public awareness and education play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of sustainable pest control practices. By raising awareness about the potential risks associated with conventional pest control methods, such as the overuse of pesticides, individuals can be encouraged to explore alternative approaches like IPM and biological control. Education campaigns can provide information on pest identification, prevention techniques, and the benefits of adopting ecologically friendly pest control practices.
Supporting Research and Innovation
Public awareness and support are crucial in advocating for increased funding and resources for pest research and innovation. Climate change presents new challenges for pest management, requiring ongoing research to understand the impacts and develop effective strategies. By supporting research initiatives and innovation, individuals and communities can contribute to the development of sustainable and effective pest control solutions that can mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Policy Implications and International Cooperation
Climate Change Policies and Pest Management
Effective pest management strategies require alignment with climate change policies and initiatives. National and international climate change policies need to recognize the importance of pest management in maintaining food security, protecting public health, and preserving biodiversity. Integration of pest management considerations into climate change adaptation and mitigation plans can help address the challenges posed by pests in a changing climate.
Collaboration on Global Pest Control Efforts
The impacts of climate change on pests are not confined to national boundaries. Global collaboration and cooperation are crucial for addressing the challenges posed by pests in a changing climate. Information sharing, collaborative research projects, and the exchange of best management practices can enhance pest control efforts and increase resilience in the face of climate change. International organizations, governments, researchers, and stakeholders need to work together to develop strategies and initiatives that transcend borders.
Funding and Support for Pest Research Projects
Funding and support for pest research projects are vital for understanding the complex interactions between climate change and pests. Government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and research institutions need to allocate resources to conduct research on the impacts of climate change on pests, develop innovative pest control strategies, and promote sustainable pest management practices. Funding and support are also necessary for training pest control professionals, disseminating research findings, and implementing effective pest management programs.
Conclusion
Climate change has far-reaching implications for pest behavior, pest control strategies, and the management of pest-related issues. Rising temperatures, shifts in geographic distributions, changes in lifecycles, and increased resistance to pesticides all contribute to the challenges posed by pests in a changing climate. In agriculture, urban environments, and disease control efforts, climate change exacerbates existing problems and creates new ones. However, by adopting sustainable pest management practices, promoting public awareness, supporting research and innovation, and fostering international cooperation, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change on pests and develop resilient solutions for pest control in a changing world.


I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.