In “Pest Control In Agricultural Supply Chains,” you will discover valuable insights and strategies to effectively manage pests in the agricultural supply chain. With a focus on educating visitors about pest control solutions, this high-quality pest control blog aims to provide helpful information while also offering product recommendations in the “Product Reviews” category. Discover ways to tackle pest-related challenges in agricultural supply chains and find the right products to ensure the smooth and effective functioning of farms and businesses.
Importance of Pest Control in Agricultural Supply Chains
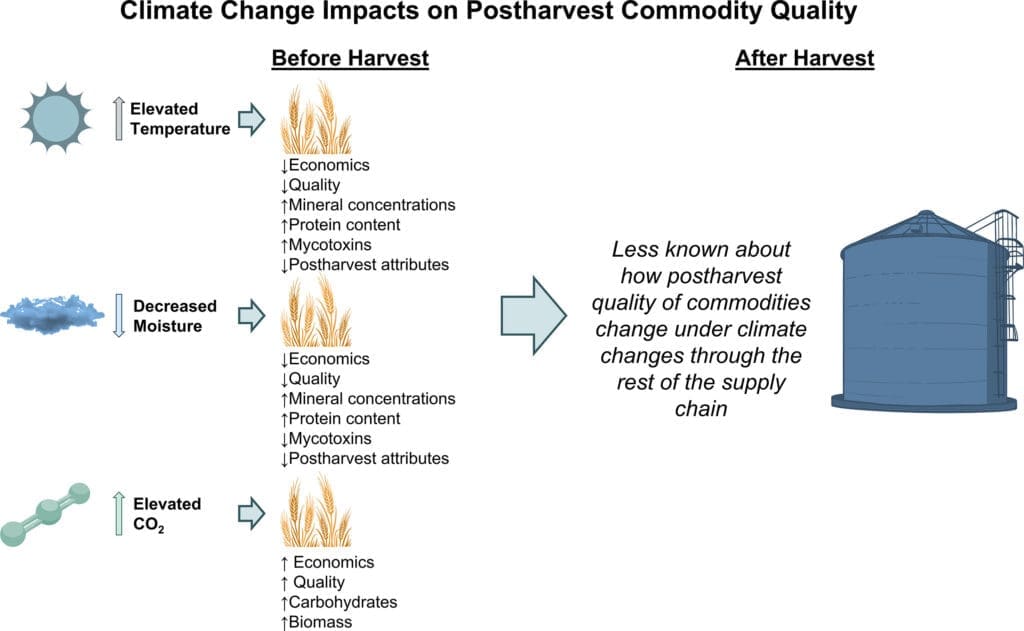
When it comes to the agricultural supply chains, pest control plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation and success of the entire system. Pest infestations can lead to significant crop loss and damage, compromising the overall productivity and profitability of the industry. Additionally, pests can contaminate the produce, posing risks to food safety and quality. By implementing effective pest control measures, agricultural supply chains can minimize economic losses, protect crops, and ensure the delivery of safe and high-quality food products.
Reducing crop loss and damage
Insects, rodents, birds, and weeds are common pests that can wreak havoc in agricultural supply chains. These pests have the potential to cause extensive damage to crops, leading to significant losses for farmers and suppliers. Insects, such as aphids and caterpillars, can devour leaves and fruits, leading to decreased yields and poor crop quality. Rodents, such as rats and mice, are notorious for gnawing on crops and stored grains, resulting in substantial losses. Birds, particularly those that feed on fruits or grains, can cause considerable damage to the crops. Weeds, on the other hand, compete with desired plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight, reducing crop yields. Proper pest control measures can effectively reduce crop loss and damage caused by these pests, ensuring a stable and abundant food supply.
Ensuring food safety and quality
Pests in agricultural supply chains not only cause physical damage to crops but also pose risks to food safety and quality. Insects and rodents can contaminate produce with their droppings, hair, and pathogens they carry. These contaminants can result in foodborne illnesses and compromise the quality of the food products. Birds, with their droppings and feathers, can also contaminate crops, thereby jeopardizing food safety. Additionally, weeds can harbor pests and diseases, further impacting the quality of the produce. By implementing effective pest control measures, agricultural supply chains can ensure that the food products they deliver are safe for consumption and of high quality.
Minimizing economic losses
Pests can cause significant economic losses in agricultural supply chains. Crop loss and damage can result in decreased yields, leading to financial setbacks for farmers and suppliers. Additionally, the presence of pests can reduce the market value of the produce due to quality issues. For example, insect-infested fruits or vegetables may not meet the required standards for sale, leading to lower prices. Furthermore, the need for corrective actions and pest control interventions can incur additional costs. By prioritizing pest control in agricultural supply chains, stakeholders can minimize economic losses and maintain profitability in the industry.
Common Pests in Agricultural Supply Chains
In agricultural supply chains, various types of pests pose threats to the crops and the overall productivity of the system. Understanding the common pests and their characteristics is essential for effective pest control management. Here are some of the most prevalent pests encountered in agricultural supply chains:
Insects
Insects are a diverse group of pests that can cause significant damage to crops. They can feed on leaves, stems, fruits, and roots, leading to reduced yields and poor crop quality. Common insect pests include aphids, caterpillars, beetles, mites, and whiteflies. Each insect species has its own unique feeding habits and life cycle, requiring specific pest control measures for effective management.
Rodents
Rodents, such as rats and mice, are common pests in agricultural supply chains. These rodents can cause substantial damage by gnawing on crops, stored grains, and infrastructure, leading to significant economic losses. They can contaminate harvested crops with their droppings and urine, posing risks to food safety. Rodents are highly adaptable and reproduce quickly, making it essential to implement preventive measures and proactive pest control strategies.
Birds
Birds, particularly those that feed on fruits or grains, can pose significant challenges in agricultural supply chains. They can cause damage by pecking at fruits, eating seeds, or contaminating crops with their droppings and feathers. Pest birds like pigeons, starlings, and sparrows are known to form large flocks, exacerbating the damage they can cause. Effective bird control measures, including deterrents and exclusion techniques, are essential to protect crops and minimize losses.
Weeds
Weeds are unwanted plants that interfere with the growth and development of desired crops. They compete with cultivated plants for resources such as nutrients, water, and sunlight, resulting in reduced crop yields. Weeds can also serve as hosts for pests and diseases, further impacting the overall health and productivity of the agricultural system. Effective weed management practices, including the use of herbicides, cultural methods, and crop rotation, are essential for controlling weed populations and minimizing their negative effects.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach that focuses on preventing and managing pest problems while minimizing the use of pesticides. It involves combining various pest control strategies to achieve effective and sustainable pest management in agricultural supply chains. The key principles of IPM include:
Definition and principles of IPM
IPM is a systematic and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management that integrates multiple strategies to suppress pest populations and minimize their impact. The principles of IPM include monitoring and identifying pests, setting action thresholds, applying appropriate pest control measures, evaluating the effectiveness of the pest management strategies, and implementing ongoing preventive measures. The goal of IPM is to achieve long-term pest control while minimizing risks to human health and the environment.
Benefits of implementing IPM in supply chains
Implementing IPM in agricultural supply chains offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it reduces the reliance on pesticides, minimizing the risks associated with their use, such as environmental contamination and the development of pesticide resistance. IPM also promotes ecosystem balance by considering the interactions between pests, beneficial organisms, and the environment. By utilizing a combination of pest control strategies, IPM can effectively manage pest populations and prevent pest resurgence. Additionally, IPM contributes to the production of safe and high-quality food products, ensuring consumer confidence and satisfaction.
Key components of IPM
The successful implementation of IPM in agricultural supply chains relies on several key components. These include:
1. Monitoring and scouting
Regular monitoring and scouting of pest populations are essential for determining the presence, abundance, and potential damage caused by pests. By closely monitoring the pest populations, supply chain stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding pest control interventions.
2. Pest identification
Accurate identification of pests is crucial for implementing targeted pest control measures. Different pests require specific control strategies, and misidentification can lead to ineffective pest management. Proper pest identification allows for the selection of appropriate control methods.
3. Cultural practices
Cultural practices, such as crop rotation, selection of pest-resistant varieties, and timing of planting, can help prevent or reduce pest infestations. These practices create unfavorable conditions for pests, making it more difficult for them to establish and thrive in agricultural supply chains.
4. Biological control
Biological control involves the use of natural enemies, such as predator insects, parasites, or pathogens, to suppress pest populations. By introducing or enhancing the activity of beneficial organisms, agricultural supply chains can achieve sustainable and environmentally-friendly pest management.
5. Mechanical and physical control
Mechanical and physical control methods involve the use of physical barriers, traps, or mechanical devices to prevent pests from accessing crops or to physically remove pest populations. These methods are often targeted, reducing the need for widespread pesticide use.
6. Chemical control
While minimizing pesticide use is a goal of IPM, there may be situations where chemical control is necessary. In such cases, the judicious use of pesticides, including selecting the appropriate pesticide, applying the correct dosage, and following safety protocols, is essential to minimize risks and achieve effective pest control.
By implementing these key components of IPM, agricultural supply chains can manage pests effectively and achieve sustainable pest control while minimizing environmental impact and preserving the quality of the produce.
Preventive Measures for Pest Control in Agricultural Supply Chains
Prevention is a crucial aspect of pest control in agricultural supply chains. By implementing preventive measures, stakeholders can reduce the risk of pest infestations and minimize the need for costly pest control interventions. Here are some preventive measures that can help control pests in agricultural supply chains:
Crop rotation and diversification
Crop rotation and diversification involve alternating different crops in the same field or across different fields on a regular basis. This practice disrupts the life cycle of pests that are specific to certain crops, reducing their populations. Additionally, crop diversification creates a more favorable ecosystem for beneficial organisms, such as predators and parasites, which help control pest populations naturally.
Sanitation practices
Maintaining proper sanitation practices in agricultural supply chains is essential for preventing pests. This includes regular removal of crop residues, weeds, and debris that can serve as breeding grounds or hiding places for pests. Proper waste management, including the prompt removal and disposal of discarded crops or damaged produce, is crucial to prevent pests from feeding and multiplying.
Proper storage and handling
Proper storage and handling of harvested crops are crucial for preventing pest infestations. Stored grains and produce should be kept in clean, dry, and well-ventilated areas to minimize favorable conditions for pests. Regular inspections and monitoring of stored products can help detect early signs of pest activity, allowing for timely responses and interventions.
Use of physical barriers
Physical barriers can be effective in preventing pests from accessing crops. Fencing, netting, or screens can be used to create physical barriers that deter pests, such as birds or insects, from entering agricultural fields or storage areas. This method can help protect crops without the need for widespread pesticide application.
Implementing good agricultural practices
Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) encompass a range of practices designed to maximize crop productivity while minimizing the impact on the environment and human health. By implementing GAPs, including proper irrigation, fertilization, and pest management, agricultural supply chains can create optimal growing conditions for crops and reduce the vulnerability to pest infestations. Training programs and certifications, such as Global GAP, can help ensure the adoption of these practices throughout the supply chain.
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of pest infestations in agricultural supply chains. By focusing on prevention, stakeholders can save costs associated with pest control interventions, protect crop quality, and maintain a sustainable and pest-free environment.
Chemical Pest Control Methods
While the use of pesticides should be minimized in agricultural supply chains, there are situations where chemical control becomes necessary. When properly used, pesticides can be effective in managing pest populations and preventing economic losses. Here are some key aspects of chemical pest control methods:
Types of pesticides used in agricultural supply chains
A wide range of pesticides is used in agricultural supply chains to control pests. These include insecticides, herbicides, fungicides, and rodenticides. Insecticides are used to control insect pests, while herbicides target undesirable weeds. Fungicides are used to prevent and manage fungal diseases, and rodenticides are used to control rodent populations. The selection of the appropriate pesticide depends on the target pest and the specific crop or situation.
Risk assessments and safety measures
Before using pesticides in agricultural supply chains, risk assessments should be conducted to evaluate the potential risks to human health and the environment. Pesticide labels should be carefully read and followed, ensuring that the products are used as intended and according to the specific crop or situation. Safety measures, such as wearing appropriate protective clothing, using calibrated equipment, and following application guidelines, should be strictly adhered to during pesticide application.
Proper application and dosage
Proper application techniques and dosages are critical for effective pest control and minimizing the risks associated with pesticide use. The application method, equipment, and timing should be appropriate for the target pest and the specific crop. Over-application or under-application of pesticides can lead to inefficiency or unintentional harm to non-target organisms. Calibration of equipment and thorough training of applicators can help ensure accurate and effective pesticide application.
While chemical pest control methods can be effective, it is important to use them judiciously and as a last resort. Minimizing pesticide use through the adoption of alternative pest management strategies and preventive measures can help protect the environment, preserve beneficial organisms, and maintain the sustainability of agricultural supply chains.
Biological Pest Control Methods
Biological pest control methods utilize natural enemies of pests to manage their populations. This approach offers an environmentally-friendly and sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides. Here are some key aspects of biological pest control methods:
Introduction to biological control
Biological control involves the use of natural enemies, including predator insects, parasites, and pathogens, to suppress pest populations. The natural enemies can be introduced, conserved, or enhanced to achieve effective pest control in agricultural supply chains. Examples of biological control agents include ladybugs, lacewings, nematodes, and certain fungi. These organisms prey on or infect pests, reducing their populations and preventing widespread damage to crops.
Using natural enemies to control pests
In some cases, natural enemies of pests can be introduced into agricultural supply chains to control pest populations. This can be done by releasing beneficial organisms, such as parasitic wasps or predatory mites, at the appropriate time and in the right locations. These natural enemies target specific pests and provide long-term pest control without the need for chemical pesticides. The conservation of natural enemies, such as by creating habitats or providing food sources, can also enhance their presence and effectiveness in controlling pests naturally.
Benefits and limitations of biological control
Biological control methods offer several advantages in agricultural supply chains. Firstly, they are environmentally-friendly, as they do not rely on chemical pesticides that can harm beneficial organisms and impact the ecosystem. Biological control agents are often highly specific to certain pests, ensuring targeted pest control without affecting non-target organisms. Additionally, biological control can provide long-term and sustainable pest management, reducing the need for frequent interventions and minimizing economic losses.
However, there are limitations to biological control methods. The effectiveness of natural enemies can vary depending on the environmental conditions, timing, and pest populations. It may take time to establish a balanced ecosystem where the natural enemies can effectively control pest populations. In certain situations, the use of supplemental control measures, such as physical barriers or alternative pest control methods, may be required for optimal pest management.
By incorporating biological pest control methods into agricultural supply chains, stakeholders can achieve sustainable and environmentally-friendly pest management. It is important to understand the biology and behavior of both pests and natural enemies to implement effective biological control strategies.

Monitoring and Early Detection of Pests
Monitoring and early detection are essential components of effective pest control in agricultural supply chains. Early intervention can prevent pest populations from reaching damaging levels and reduce the need for more drastic control measures. Here are some key aspects of monitoring and early detection of pests:
Developing effective monitoring systems
Effective monitoring systems involve regular inspections and assessments of agricultural fields, storage areas, and processing facilities. Monitoring can be done visually, through direct observation, or by using specific tools and traps designed to capture or detect pests. The frequency and intensity of monitoring depend on the specific crop, pest pressure, and the goals of pest management.
Utilizing pest surveillance techniques
Pest surveillance techniques can provide valuable information about pest populations and their behavior. This includes the use of pheromone traps, sticky traps, and visual surveys to monitor pest activity and abundance. Surveillance techniques can help identify hotspots of pest infestations, allowing for targeted pest control interventions. By collecting data on pest populations and their dynamics, supply chain stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding pest control measures.
Early detection methods for rapid response
Early detection of pests is crucial for rapid response and effective pest control. Early signs of pest infestation, such as pest eggs, nymphs, or initial plant damage, should be promptly identified and addressed. By taking immediate action, such as removing or treating infested plants or implementing cultural control measures, pest populations can be suppressed before they can cause extensive damage. Rapid response measures can help prevent pest outbreaks and minimize economic losses in agricultural supply chains.
By implementing rigorous monitoring and early detection practices, agricultural supply chains can stay proactive in pest management. Regular monitoring allows for timely intervention and the implementation of appropriate pest control strategies, ensuring the health and productivity of crops.
Quarantine and Biosecurity Measures
Quarantine and biosecurity measures play a crucial role in preventing the introduction and spread of pests in agricultural supply chains. By implementing strict protocols and maintaining a pest-free environment, stakeholders can protect crops, ensure the integrity of the supply chain, and maintain the reputation of the industry. Here are some key aspects of quarantine and biosecurity measures:
Importance of quarantine in preventing pest introduction
Quarantine measures are designed to prevent the entry and establishment of pests from outside sources. This involves strict inspection and control procedures for incoming commodities, machinery, equipment, and live plant materials. Quarantine stations and facilities are essential for the detection, identification, and treatment of potential pests before they can spread within agricultural supply chains. Quarantine protocols are crucial to prevent the introduction of invasive species, pests, or diseases that can have devastating impacts on crops and the ecosystem.
Implementing biosecurity protocols
Biosecurity protocols aim to prevent the spread of pests, diseases, and other biological threats within agricultural supply chains. This involves implementing strict control measures, such as limiting access to production areas, disinfection of equipment and vehicles, and proper waste disposal. Controlling human traffic and implementing hygiene practices, including handwashing and wearing protective clothing, can also contribute to maintaining biosecurity. Training and education programs are essential for ensuring that all personnel involved in the supply chains adhere to biosecurity protocols.
Role of certification in ensuring pest-free supply chains
Certification programs, such as phytosanitary certification, can help ensure pest-free supply chains. These programs involve rigorous inspections, testing, and documentation to verify the absence of pests and diseases in crops and commodities. Phytosanitary certificates provide assurance to buyers, importers, and consumers that the produce has undergone strict pest control measures and is safe for consumption. Certifications contribute to the credibility and marketability of agricultural supply chains, supporting the overall success of the industry.
By implementing quarantine and biosecurity measures, agricultural supply chains can prevent the introduction and spread of pests, diseases, and invasive species. Strict control protocols, inspections, and certifications help maintain the integrity of the supply chains and ensure the delivery of pest-free and high-quality agricultural products.
Training and Education for Pest Control in Supply Chains
Training and education are essential components of effective pest control in agricultural supply chains. By providing knowledge and skills in pest identification, management, and best practices, stakeholders can enhance their ability to prevent and control pests. Here are some key aspects of training and education for pest control:
Providing education on pest identification and management
Education on pest identification is crucial for stakeholders involved in agricultural supply chains. This includes farmers, farm workers, agronomists, and personnel involved in storage and processing facilities. Proper identification of pests and their life stages allows for targeted control measures and appropriate intervention strategies. Training programs should provide information on pest biology, behavior, and the signs of infestation, enabling stakeholders to take early action and prevent further damage.
Training programs for farmers and supply chain workers
Training programs should be developed to cover various aspects of pest control in agricultural supply chains. These programs can include topics such as integrated pest management practices, preventive measures, pesticide safety, and application techniques. Practical training sessions may include hands-on activities, field demonstrations, and the use of simulation tools. By providing comprehensive training programs, stakeholders can enhance their pest control knowledge, improve their skills, and effectively implement pest management strategies.
Raising awareness about pest control best practices
Raising awareness about pest control best practices is essential for the success of pest management in agricultural supply chains. This can be achieved through educational campaigns, workshops, or outreach programs targeting farmers, consumers, and the general public. Promoting the importance of pest control, the benefits of integrated pest management, and the impact of pests on food safety and quality can increase understanding and support for pest control initiatives. The dissemination of information through various channels, such as websites, social media, and community events, can help reach a wider audience and generate awareness about the importance of pest control.
By investing in training and education programs, agricultural supply chains can build capacity and ensure continuous improvement in pest control practices. Knowledgeable and well-trained stakeholders are better equipped to prevent, detect, and manage pest infestations, contributing to the overall success and sustainability of the industry.
Emerging Technologies in Pest Control
Emerging technologies offer innovative solutions for pest control in agricultural supply chains. These technologies can enhance the efficiency, precision, and effectiveness of pest management strategies. Here are some key emerging technologies in pest control:
Use of drones for pest monitoring and spraying
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can be used for aerial monitoring of agricultural fields. They provide real-time images and data on crop health, pest populations, and potential areas of infestation. This allows for targeted interventions and optimal use of pest control measures. Drones can also be used for precision spraying of pesticides, reducing the amount of chemicals used and minimizing the impact on the environment.
Application of machine learning and artificial intelligence
Machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies can analyze large amounts of data, including pest behavior, environmental factors, and crop conditions. This data-driven approach can provide insights and predictive models for effective pest management. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and correlations, helping stakeholders make informed decisions regarding pest control strategies, timing, and resource allocation.
Precision agriculture for targeted pest control
Precision agriculture combines technologies, including GPS, sensors, and data analytics, to optimize agricultural practices. This includes the targeted application of pest control measures based on specific pest locations or concentrations. Variable rate technology allows for precise and customized pesticide application, reducing chemical usage and minimizing potential negative impacts. By implementing precision agriculture practices, agricultural supply chains can achieve efficient and sustainable pest control management.
The emergence of these technologies offers exciting opportunities for pest control in agricultural supply chains. While these technologies can enhance pest management practices, it is important to ensure that their implementation is guided by proper regulations, safety measures, and ethical considerations.
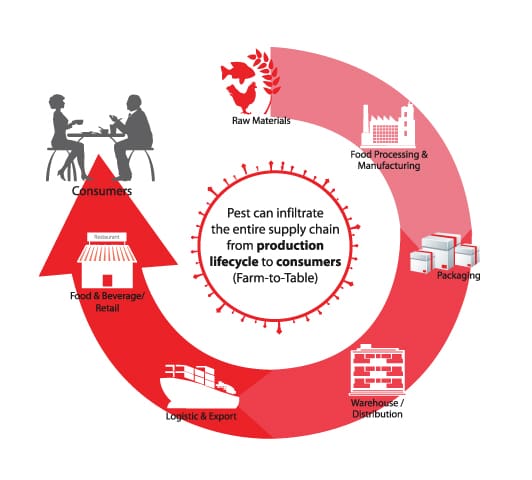
In conclusion, pest control in agricultural supply chains is of utmost importance to ensure the smooth operation, productivity, and safety of the industry. By reducing crop loss and damage, ensuring food safety and quality, and minimizing economic losses, effective pest control measures contribute to the success and sustainability of agricultural supply chains. Through the implementation of integrated pest management, preventive measures, effective monitoring, and the use of emerging technologies, stakeholders can protect crops, promote environmental sustainability, and deliver high-quality food products to consumers. Investing in training and education programs further enhances the capacity of stakeholders to prevent, detect, and manage pests, supporting the overall goal of a pest-free and thriving agricultural industry.

I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.