Have you ever wondered how pest control methods have evolved throughout history? In this article, we will take a fascinating journey through time to explore the historical evolution of pest control methods. From ancient civilizations to modern times, we will discover the ingenious techniques and remedies that have been used to combat pests and protect our homes and crops. Join us as we delve into the past to uncover the fascinating stories behind the methods we use today.
1. Ancient Pest Control
1.1 Early forms of pest control
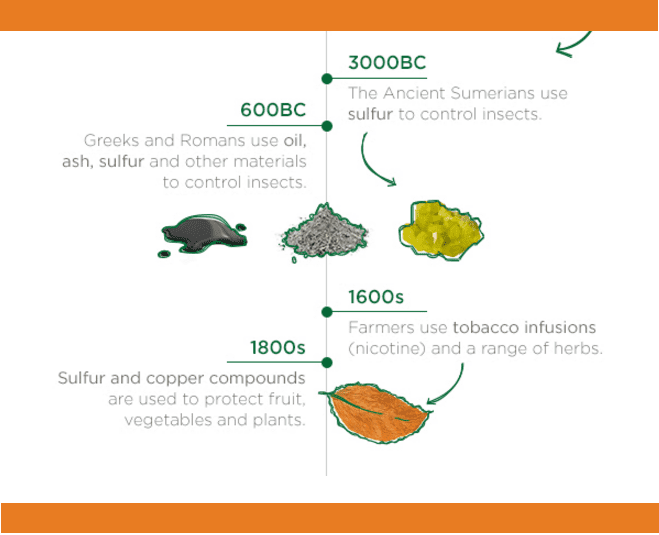
In ancient times, people faced numerous challenges when it came to dealing with pests. However, they showed remarkable ingenuity in creating various pest control methods. Early forms of pest control can be traced back thousands of years, and they often involved simple yet effective techniques. For instance, some ancient civilizations utilized natural deterrents such as smoke and certain aromatic plants to repel insects and rodents from their living spaces.
1.2 Ancient Egyptian pest control
The ancient Egyptians were known for their advanced civilization, and they had developed unique methods for pest control as well. They understood the importance of preventing pests from damaging their crops and spreading diseases. To protect their agricultural fields, the Egyptians used traps, sticky substances, and barriers made from reeds to keep insects away. Additionally, the usage of cats for rodent control was prevalent in ancient Egypt.
1.3 Pest control in ancient Greece and Rome
In ancient Greece and Rome, pest control methods became more sophisticated. Greek philosopher and scientist Aristotle observed that certain plants had the ability to repel pests, and this knowledge was put to use by farmers. Additionally, the Greeks and Romans made use of various traps, nets, and poisons to control pests. The Roman writer Pliny the Elder even recorded the use of sulfur and pitch to repel insects.
2. Medieval and Renaissance Approaches
2.1 Pest control during the Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, pest control methods were largely influenced by superstitious beliefs and religious practices. People relied heavily on folklore and the use of amulets, herbs, and other natural remedies to fend off pests. However, the knowledge of pest control also expanded during this period, with advancements in agricultural practices. Crop rotation and the introduction of certain plants as natural insecticides were key developments during the Middle Ages.
2.2 The Renaissance and advancements in pest control
The Renaissance period marked a resurgence of scientific thought and experimentation, leading to significant advancements in pest control. Scholars like Leonardo da Vinci studied insects and their habits, providing valuable insights into pest behavior. During this time, European farmers began using traps, insect-repelling plants, and even introduced predators to control pests. The Renaissance also saw the emergence of early pest control manuals, offering advice and guidance to farmers.

3. Early Modern Pest Control Methods
3.1 The development of chemical pesticides
The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed a significant shift in pest control methods with the development of chemical pesticides. This period marked the beginning of synthetic insecticides, such as pyrethrum and nicotine sulfate. These chemical compounds were highly effective in targeting specific pests, but their widespread use also led to unintended ecological consequences.
3.2 Early forms of biological pest control
Concurrent with the development of chemical pesticides, early forms of biological pest control also emerged during this period. Scientists and farmers recognized the potential of using natural enemies, such as parasitoids and predators, to control pests. Ladybugs, for example, were widely introduced to combat aphid infestations. This marked a shift towards more environmentally friendly pest control methods, focusing on natural and sustainable solutions.
3.3 Pest control in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant advancements in technology, which influenced pest control methods as well. Agricultural machinery and improved irrigation systems led to more efficient farming practices. Furthermore, the development of steam and gas-powered equipment enabled the mass production and distribution of chemical pesticides. However, the increased reliance on pesticides during this time also raised concerns about their impact on the environment and human health.

4. Pioneers of Modern Pest Control
4.1 The discovery and use of DDT
The discovery of DDT in the mid-20th century marked a significant milestone in the field of pest control. DDT was a highly effective insecticide and played a crucial role in combating diseases such as malaria and typhus. Its use resulted in a sharp decline in mosquito populations and the eradication of diseases in many regions. However, the long-lasting nature of DDT and its adverse effects on the environment eventually led to its ban in several countries.
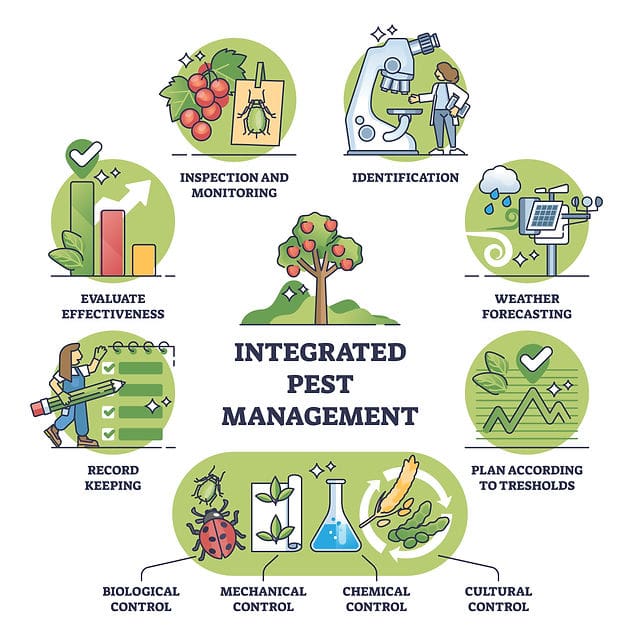
4.2 The introduction of integrated pest management
In response to the environmental concerns raised by the excessive use of pesticides, Integrated pest management (IPM) was introduced. IPM is a holistic approach that combines various pest control strategies, including biological controls, cultural practices, and the targeted use of pesticides. This approach aims to minimize the reliance on chemical pesticides and encourages the adoption of sustainable practices. IPM has proven to be highly effective in managing pests while minimizing environmental impact.
4.3 The Green Revolution and advancements in pest control
The Green Revolution, which began in the mid-20th century, brought about significant advancements in agricultural practices and pest control. The development of high-yield crop varieties and the widespread use of fertilizers and irrigation led to increased food production. Pest control methods also evolved during this period, with the introduction of genetically modified crops resistant to pests and diseases. These advancements helped address food security concerns but also sparked debates about the potential risks associated with genetically modified organisms.
5. Contemporary Pest Control Methods
5.1 Environmental concerns in pest control
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly pest control methods. Awareness about the negative impacts of chemical pesticides on ecosystems and human health has led to a shift towards less toxic alternatives. Integrated pest management continues to gain popularity as it promotes the use of natural predators, crop rotations, and cultural practices to manage pests effectively.
5.2 The use of pheromones and traps
Pheromones, which are chemicals released by insects to communicate with each other, have been harnessed as a pest control tool. Pheromone traps are used to attract insects and disrupt their mating patterns, thereby reducing population growth. These traps have shown promising results in controlling pest species while minimizing environmental impact and reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
5.3 Pest control in agriculture
Agricultural pest control remains a crucial aspect of food production. Farmers now have access to a wide range of pest control methods, including biological agents, insect-resistant crop varieties, and precision farming techniques. Integrated pest management practices continue to be widely adopted to strike a balance between pest control effectiveness and environmental sustainability.
5.4 Pest control in urban areas
Pest control in urban areas poses unique challenges, often requiring specialized techniques and tailored solutions. Integrated pest management practices have been applied to effectively manage pests in cities, including the use of physical barriers, improved waste management, and the targeted use of pesticides. Additionally, education and awareness campaigns play a vital role in engaging residents and promoting proactive pest control measures.
6. Future Trends in Pest Control
6.1 Emerging technologies in pest control
The future of pest control holds promises of advanced technologies that can revolutionize the industry. Innovations such as remote sensing, drones, and artificial intelligence are being explored to enhance pest monitoring and management. These technologies offer the potential for more targeted and precise pest control strategies, reducing the need for broad-spectrum chemical pesticides.
6.2 The role of genetics in pest control
Advancements in genetics hold potential for genetically modifying pest species to control their populations. Techniques like the sterile insect technique and gene editing can disrupt pest reproduction and reduce their numbers. However, the ethical considerations and potential ecological consequences of these technologies must be carefully evaluated before widespread implementation.
6.3 Sustainable pest control solutions
The future of pest control will likely see an increased focus on sustainable and eco-friendly solutions. The development of biopesticides derived from natural sources, the use of pheromones and traps, and the adoption of precision farming techniques will contribute to the shift towards more environmentally conscious pest control practices. The goal is to find a balance between effective pest management and preserving biodiversity, ensuring a sustainable future for both humans and the environment.
In summary, pest control methods have evolved significantly throughout history, from early forms of pest control in ancient civilizations to the development of chemical pesticides and the adoption of integrated pest management. The focus has shifted towards environmentally friendly approaches in recent years, with a growing emphasis on natural predators, pheromones, and sustainable farming practices. The future of pest control holds promises of advanced technologies and genetic solutions, aiming to strike a balance between effective pest management and ecological sustainability.

I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.