In today’s ever-changing world, the delicate balance of pest control has become increasingly crucial. As we strive to maintain a pest-free environment, it is essential to recognize the vital role that bees play in this process. Bees are not just prolific pollinators, but they also contribute to pest control in ways that often go unnoticed. By understanding the importance of bee conservation, we can ensure the continued harmony between pests and their natural predators, ultimately creating a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for pest control.
The Role of Bees in Agriculture
Bees play a crucial role in agriculture through their valuable contribution to crop pollination. As they collect nectar from various plants, bees inadvertently pick up pollen grains on their bodies and transfer them from one flower to another, aiding in the fertilization process. This process, known as pollination, is essential for the reproduction of many flowering plants, including numerous crops that humans rely on for food production.
Pollination of crops
The pollination services provided by bees are vital for numerous crops, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds. Certain plants, such as apples, cherries, and blueberries, heavily rely on insect pollinators like bees to ensure successful fruit set. Without bees, the yield and quality of these crops would be significantly diminished.
Increasing crop yield
By facilitating pollination, bees help to increase crop yields. Studies have shown that the presence of bees in agricultural fields can enhance fruit set, leading to higher yields of crops. In some cases, this can even result in a significant increase in profitability for farmers. The role of bees in agriculture is not only crucial for food production but also for the economic well-being of farmers.
Diverse pollination abilities
One of the remarkable aspects of bees’ role in agriculture is their ability to pollinate a wide variety of crops. Bees are generalist pollinators, meaning they can thrive on and pollinate multiple types of flowering plants. The diversity of crops that bees can pollinate is essential for maintaining the stability and resilience of agricultural systems. Bees’ flexible pollination abilities ensure that a vast range of crops can be successfully cultivated.
The Decline of Bee Populations
Despite their immense importance, bee populations have been declining at an alarming rate in recent years. This decline has been attributed to various factors, each contributing to the overall decrease in bee numbers across the globe.
Causes of bee population decline
Multiple factors have been identified as the causes of bee population decline. Habitat loss and fragmentation, pesticide exposure, climate change, and the spread of parasites and diseases all play significant roles in this phenomenon. These factors often interact and exacerbate the negative effects on bee populations, leading to a rapid decline in their numbers.
Impact on agriculture
With the decline of bee populations, agriculture faces substantial challenges. Reduced bee populations mean fewer pollinators available to assist in the fertilization of crops, which can lead to a decline in yields and crop quality. Farmers may need to invest more resources, such as hand-pollination or the introduction of alternative pollinators, to ensure adequate crop production.
Impact on ecosystem
Beyond agriculture, the decline of bee populations has far-reaching consequences for the ecosystem as a whole. Bees are key pollinators in natural ecosystems, playing a critical role in the reproduction of numerous wild plant species. The loss of bees can disrupt entire ecosystems, leading to a decline in plant diversity and affecting the food chain. The indirect impact on other pollinators, animals, and even humans can be substantial.
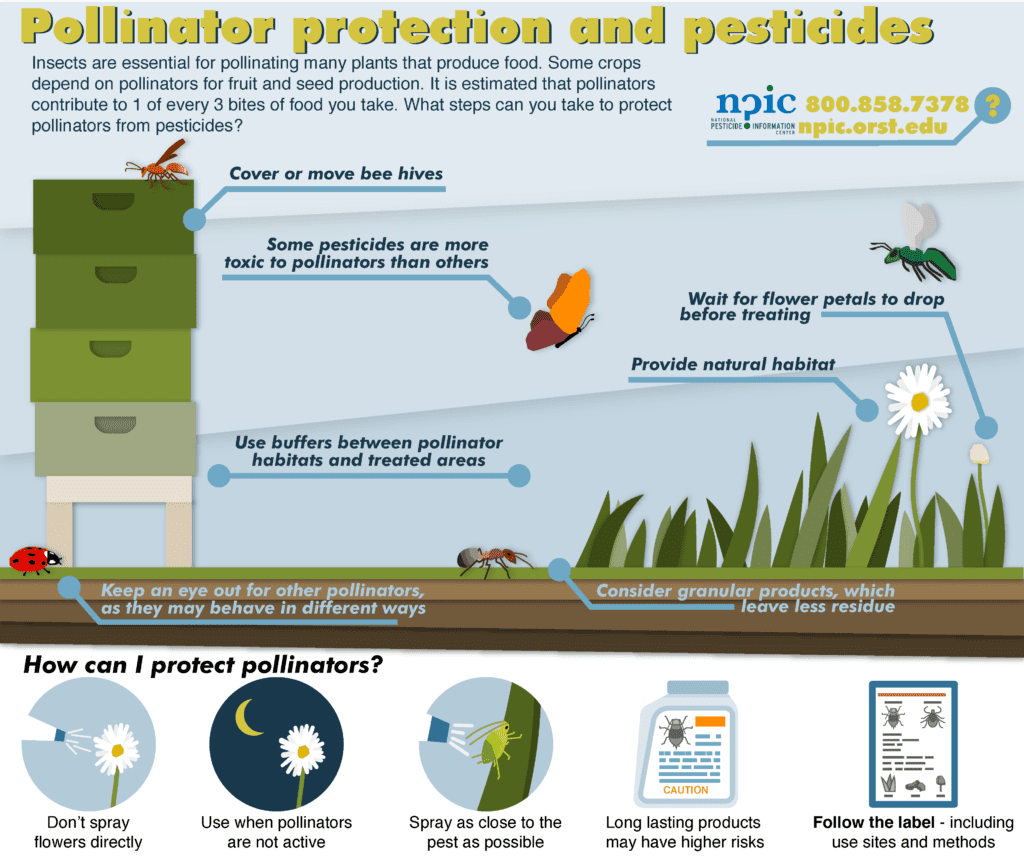
The Link Between Bee Conservation and Pest Control
Bee conservation goes beyond the preservation of a single species. Protecting and promoting bee populations can have profound effects on pest control, leading to a more sustainable and ecologically balanced approach.
Natural pest control
Bees contribute to natural pest control by predating on various insect pests. Certain bee species, such as mason bees and leafcutter bees, actively hunt for and consume insect pests, helping to regulate their populations. By encouraging the presence and diversity of bees, farmers can benefit from a natural form of pest control that reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides.
Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides
One of the major advantages of promoting bee conservation in pest control is the potential to reduce the use of chemical pesticides. Pesticides, while effective in managing pests, often have unintended negative consequences on the environment and human health. By utilizing the services of bees and other natural predators, farmers can minimize their reliance on these chemical interventions, leading to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to pest management.
Preservation of biodiversity
Bee conservation plays a crucial role in preserving biodiversity within agricultural landscapes. By promoting the presence and diversity of bees, farmers can create habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species. This biodiversity is not only beneficial for the overall health and resilience of ecosystems but also helps to maintain a balance between pests and their natural predators.
Benefits of Bee Conservation in Pest Control
The incorporation of bee conservation measures in pest control practices offers a multitude of benefits, ranging from sustainable pest management to positive impacts on human health.
Sustainable pest management
By harnessing the natural predation abilities of bees and other beneficial insects, farmers can adopt more sustainable pest management practices. Natural pest control reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides, minimizing the potential risks associated with their use. This approach promotes the long-term health of agricultural systems and helps to maintain a balance between pests and their natural predators.
Economic benefits
Integrating bee conservation in pest control can also have economic benefits for farmers. By utilizing bees as natural pollinators and pest controllers, farmers can reduce their production costs by decreasing the need for chemical inputs. Additionally, the improved yields and crop quality resulting from proper pollination and pest management can enhance profitability and contribute to a more successful farming operation.
Positive impact on human health
Protecting bee populations and promoting their role in pest control also has direct benefits for human health. As the use of chemical pesticides decreases, the exposure to potentially harmful residues on food decreases as well. Additionally, the preservation of biodiversity and the overall health of ecosystems can have indirect positive impacts on human health by promoting clean air, water, and a more balanced environment.
Implementing Bee Conservation Measures
To effectively promote bee conservation in pest control, various measures can be implemented at the individual, community, and policy levels.
Creating bee-friendly habitats
At the individual and community levels, creating bee-friendly habitats is of utmost importance. This can be done by planting a diverse range of native flowering plants that provide nectar and pollen for bees. Avoiding the use of pesticides in these designated areas and providing suitable nesting sites, such as bee houses or undisturbed soil patches, can further enhance the attractiveness of these habitats for bees.
Reducing pesticide use
Reducing pesticide use is a critical step in promoting bee conservation. Farmers can adopt integrated pest management (IPM) strategies that prioritize the use of biological control agents, including bees, to manage pest populations. Monitoring and scouting for pests, implementing cultural practices, and releasing beneficial insects are all IPM techniques that can significantly reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
Supporting local beekeepers
Supporting local beekeepers is another important aspect of promoting bee conservation. By purchasing honey and other bee-related products from local producers, consumers can contribute to the financial sustainability of beekeeping operations. Additionally, supporting initiatives that educate and train beekeepers in sustainable practices can help ensure the long-term health and well-being of bee populations.
Promoting Awareness and Education
Raising awareness and educating farmers, consumers, and local communities about the importance of bee conservation in pest control is crucial for the success of these efforts.
Educating farmers and consumers
Educating farmers about the benefits of bee conservation in pest control can help them understand the value of incorporating natural pollinators and pest controllers into their operations. Workshops, seminars, and informational materials can provide farmers with the knowledge and resources they need to implement bee-friendly practices. Similarly, educating consumers about the role bees play in agriculture and the importance of supporting bee-friendly products can foster a greater appreciation for bee conservation efforts.
Engaging with local communities
Engaging with local communities is essential in creating a supportive environment for bee conservation. Community outreach programs, public demonstrations, and interactive events can help raise awareness and foster a sense of shared responsibility for preserving bee populations. Involving schools, gardening clubs, and other community organizations can ensure that the message of bee conservation reaches a diverse audience.
Advocacy for bee conservation policies
Advocacy for bee conservation policies at the local, regional, and national levels is crucial for the long-term success of bee conservation efforts. Public support and pressure can encourage policymakers to enact and enforce regulations that protect bees and their habitats. Collaborating with environmental organizations, beekeeping associations, and other stakeholders can amplify advocacy efforts and promote meaningful change.
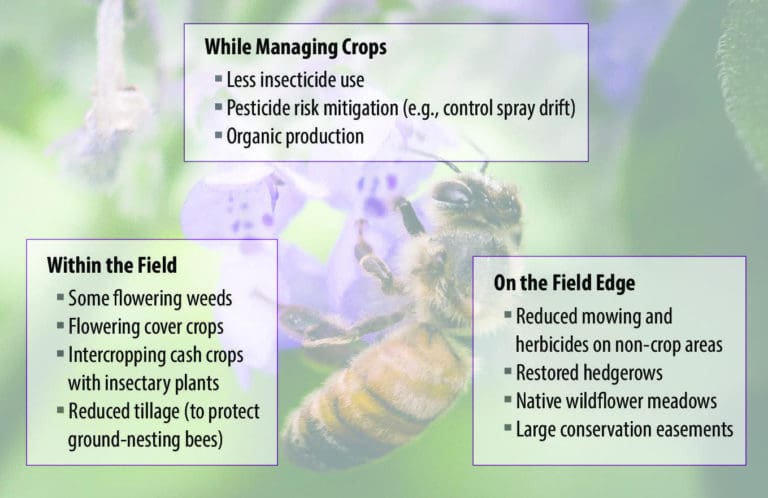
Government and Policy Initiatives
Governments and policymakers have a vital role to play in supporting bee conservation through targeted initiatives and regulations.
Incentives for bee conservation
Governments can provide incentives to farmers and beekeepers who adopt bee-friendly practices. This can include financial support or tax benefits that help offset the costs of creating and maintaining bee-friendly habitats. Such incentives can encourage widespread adoption of bee conservation measures and foster a culture of environmental stewardship among farmers.
Regulating pesticide use
Regulating pesticide use is essential in protecting bee populations. Governments can establish strict guidelines and enforce the responsible use of pesticides, particularly those known to be highly toxic to bees. By restricting the use of harmful chemicals and promoting the adoption of safer alternatives, governments can play a crucial role in safeguarding the health and well-being of bees.
Research funding for bee health
Investing in research on bee health is vital for understanding the complex interactions between bees, pests, and the environment. Governments can allocate funds to support scientific studies and initiatives aimed at improving bee health, managing diseases and parasites, and developing sustainable pest control solutions. This research can inform evidence-based policies and practices that promote the conservation of bees and their vital roles in agriculture and ecosystem health.
Collaboration between Beekeepers and Pest Control Professionals
Collaboration between beekeepers and pest control professionals can lead to effective and sustainable pest management strategies that benefit both bees and agricultural systems.
Sharing knowledge and expertise
Beekeepers and pest control professionals can collaborate by sharing their knowledge and expertise. By understanding the specific pest control needs of farmers and the natural behaviors of bees, pest control professionals can develop strategies that maximize the use of bees as beneficial insects. This collaboration can lead to the development of customized management plans that are effective, economically viable, and environmentally friendly.
Implementing integrated pest management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is an approach that combines various pest control techniques to manage pest populations effectively while minimizing the use of chemical pesticides. By integrating the use of bees as natural enemies of pests into IPM programs, pest control professionals can enhance the efficiency and sustainability of pest management strategies. This collaborative approach ensures that both chemical and natural control methods are used judiciously, leading to a more balanced and resilient pest control system.
Building sustainable partnerships
Building sustainable partnerships between beekeepers and pest control professionals is essential for long-term success. By fostering open lines of communication and cooperation, both parties can work together to monitor and manage pest populations effectively. This collaboration can result in the development of innovative pest control solutions that prioritize bee conservation, ecological sustainability, and crop productivity.
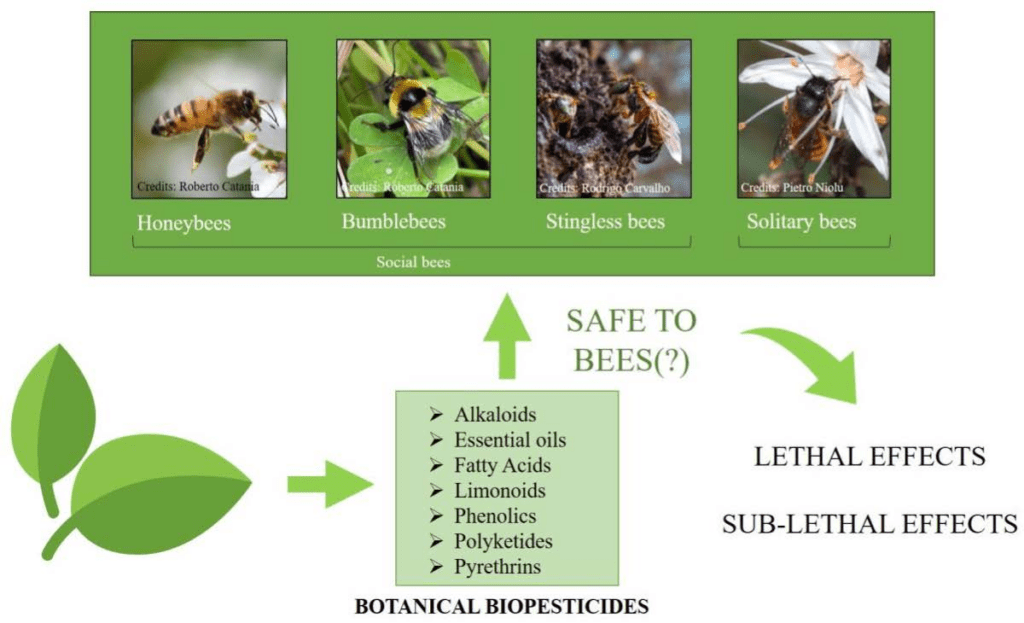
Success Stories in Bee Conservation and Pest Control
Numerous success stories illustrate the positive outcomes of implementing bee conservation measures in pest control practices.
Case studies of positive outcomes
In various agricultural regions around the world, the successful implementation of bee conservation measures has led to significant improvements in crop yields and reduced reliance on chemical pesticides. Farms that have established bee-friendly habitats and integrated bees as natural pollinators and pest controllers have witnessed higher yields, improved crop quality, and increased profitability. These case studies demonstrate the potential of bee conservation in revolutionizing pest control practices.
Example of successful collaboration
One notable example of successful collaboration between beekeepers and pest control professionals is seen in the almond industry in California. Almonds heavily rely on honeybee pollination, and the industry faced significant challenges due to widespread bee losses. By collaborating with beekeepers, almond growers developed best management practices that protected bee health while ensuring adequate pollination. This partnership has been instrumental in restoring bee populations, improving almond yields, and setting an example for other agricultural sectors.
Impacts on local ecosystems
The positive impacts of bee conservation and sustainable pest control extend beyond agricultural systems. By promoting the presence of bees and other beneficial insects, local ecosystems experience increased biodiversity and improved pollination services. This, in turn, benefits wild plant species, birds, and other animals that rely on these ecosystems. The restoration of balance and resilience within local ecosystems is a significant achievement of bee conservation efforts.
Conclusion
The role of bees in pest control is of paramount importance for agriculture, ecosystem health, and human well-being. Through their invaluable pollination services and natural pest control abilities, bees contribute to sustainable and ecologically sound pest management practices. The decline of bee populations poses significant challenges for agriculture, but collective action and the implementation of bee conservation measures can pave the way for a brighter future. By creating bee-friendly habitats, reducing pesticide use, supporting local beekeepers, and promoting awareness and education, we can ensure the preservation of bees and their vital roles. With the collaboration of governments, policymakers, farmers, beekeepers, and pest control professionals, we can achieve a harmonious balance between pest management and the conservation of bees and biodiversity. Together, we can create a resilient and sustainable agricultural system that benefits both humans and the natural world.


I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.
