In this informative article, you will discover the crucial role that soil health plays in preventing pest infestations. By understanding the importance of maintaining a healthy soil ecosystem, you can effectively minimize the risks posed by pests in your surroundings. Get ready to explore the fascinating connection between soil health and pest control, and uncover practical tips to keep your soil thriving. Let’s dive right in!
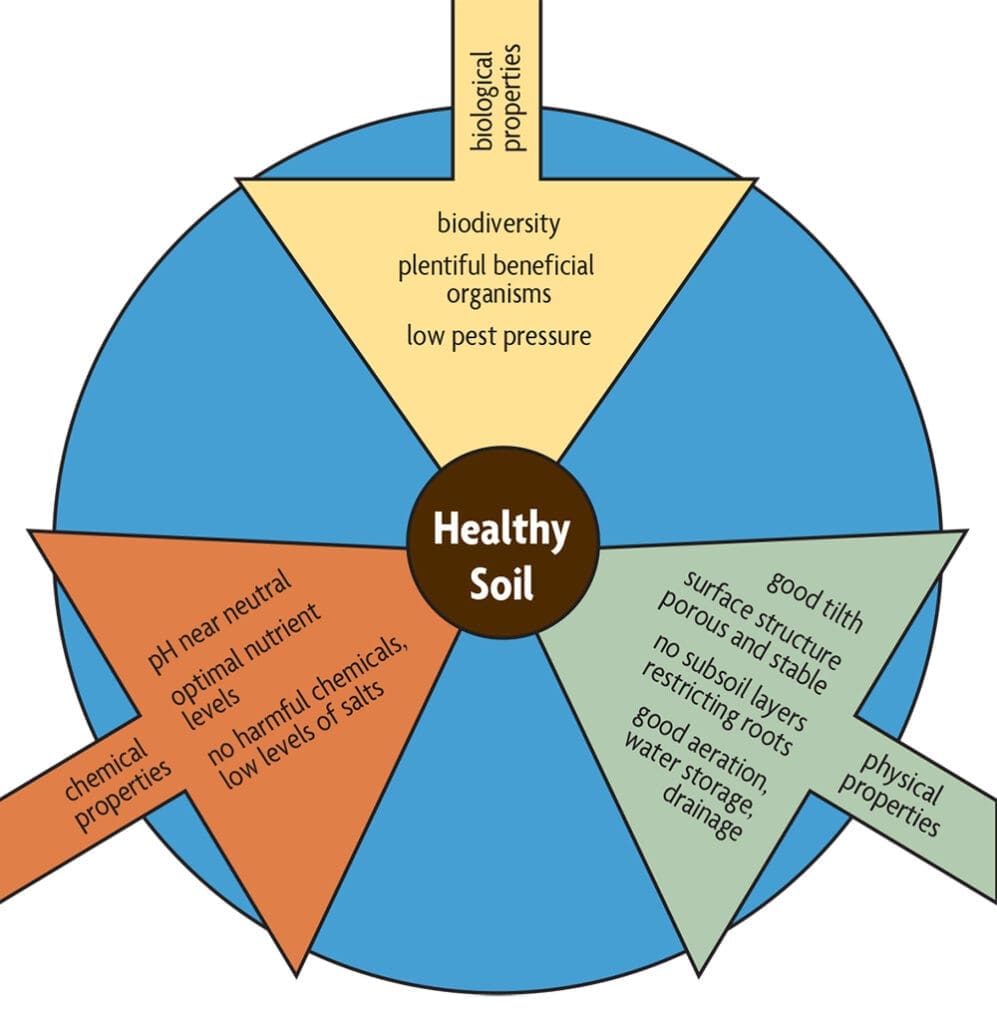
Importance of Soil Health
Maintaining healthy soil is crucial for plant growth and overall ecosystem balance. The quality and composition of soil play a significant role in preventing pest infestations and promoting sustainable pest management practices. By understanding the impact of soil health on plant growth and pest resistance, as well as implementing proper soil management techniques, you can effectively prevent and control pest infestations.
Impact of Soil Health on Plant Growth
Soil health is directly linked to the growth and productivity of plants. Healthy soil provides a suitable environment for plants to establish strong root systems, access essential nutrients, and effectively absorb water. When soil is rich in organic matter and has a balanced pH level, plants are more likely to thrive and resist pest attacks.
On the other hand, poor soil health compromises the ability of plants to develop robust root systems and access essential nutrients. Weak or stressed plants are more susceptible to pest infestations, as they lack the natural defenses that healthy plants possess. Therefore, maintaining optimal soil health is a critical factor in preventing pests from attacking your plants.
Connection between Soil Health and Pest Resistance
Soil health directly affects the ability of plants to resist pest attacks. A healthy soil ecosystem promotes beneficial soil organisms, such as earthworms and beneficial bacteria, that help control pests naturally. These beneficial organisms enhance the soil’s biological activity and create an environment that is less favorable for pests.
Additionally, healthy soil conditions create a balanced soil structure, enabling plants to grow strong and withstand pest pressures. By maximizing soil health, you can reduce the vulnerability of your plants to pests and minimize the need for chemical pest control methods.
Benefits of Healthy Soil in Pest Prevention
Healthy soil offers various benefits in preventing pests and minimizing pest infestations. Here are some notable advantages:
-
Enhanced plant immunity: Nutrient-rich soil promotes plant vigor and strengthens their natural defense mechanisms, making them more resilient to pest attacks.
-
Imbalanced pest habitat: A healthy soil ecosystem disrupts the ideal conditions for pests to thrive, reducing their population density and limiting their ability to cause significant damage.
-
Sustainable pest management: By focusing on soil health, you can adopt eco-friendly pest control practices that minimize the use of chemical pesticides, reducing environmental impact.
-
Cost-effective pest prevention: Maintaining healthy soil reduces the dependence on expensive pest control measures and ensures long-term pest management without significant financial investment.
By understanding the connection between soil health and pest resistance, you can proactively work towards improving soil conditions and prevent pest infestations before they become major issues.
Impact of Soil Composition on Pest Infestations
The composition of soil, including factors such as pH, moisture levels, and nutrient content, directly impacts the prevalence and severity of pest infestations. By understanding how these elements influence pest populations, you can take appropriate measures to manage soil composition effectively and prevent pest outbreaks.
Effect of Soil pH on Pest Populations
Soil pH plays a crucial role in determining the survival and activity of pests. Different pests thrive in specific pH ranges, and a shift in soil pH towards their preferred range can lead to increased pest populations.
For example, some pests, like root-knot nematodes, prefer acidic soil conditions. If the soil pH is too low, it creates a favorable environment for these pests to multiply rapidly and attack plant roots. Conversely, some pests, like flea beetles, thrive in alkaline soil conditions. Understanding the preferred pH ranges of common pests can help you adjust soil pH accordingly and prevent infestations.
Role of Soil Moisture in Pest Development
Moisture levels in the soil influence the life cycle and development of various pests. Excess moisture can create damp conditions that favor the growth of pests like slugs, snails, and fungal pathogens. Conversely, moisture deficits can stress plants, making them more susceptible to pest infestations.
Maintaining proper soil moisture levels is crucial for preventing pest outbreaks. Adequate drainage, irrigation practices, and mulching techniques can help regulate soil moisture, creating an environment that discourages pest development.
Relationship Between Soil Nutrients and Pest Infestations
Soil nutrient levels directly impact plant health and, consequently, their vulnerability to pests. Nutrient deficiencies or imbalances can weaken plants and compromise their natural defenses, making them more attractive targets for pests.
Certain pests, like aphids and spider mites, are attracted to plants that are deficient in essential nutrients. By ensuring your soil is nutrient-rich and supplying plants with the necessary elements, you can bolster their resilience to pests and reduce the risk of infestations.
Understanding the impact of soil composition on pest infestations allows you to make informed decisions when managing soil health. By addressing any imbalances or deficiencies in soil pH, moisture, and nutrients, you can create an environment that discourages pests and promotes healthy plant growth.
Managing Soil Health for Pest Prevention
Proactively managing soil health is key to preventing pest infestations and maintaining a healthy gardening environment. Implementing the following practices can help you create optimal soil conditions that deter pests and support plant growth.
Choosing the Right Soil Amendments
Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can significantly improve soil health. Organic matter enriches the soil with essential nutrients, enhances its water-holding capacity, and improves its structure. By incorporating organic amendments into the soil, you can create a fertile environment that promotes plant growth and prevents pest infestations.
However, it’s important to choose the right amendments for your soil type and specific plant needs. Conducting a soil test can provide valuable insights into nutrient deficiencies and help you select the appropriate amendments to improve soil health effectively.
Implementing Proper Soil Drainage Techniques
Good soil drainage is crucial for preventing waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and attract soil-dwelling pests. It’s important to ensure that your garden beds have proper drainage systems in place.
Raised beds, for example, can help improve soil drainage by elevating the growing area above ground level. Additionally, incorporating organic matter into the soil can enhance its drainage properties. By maintaining proper soil drainage, you create a less favorable environment for pests that thrive in damp conditions.
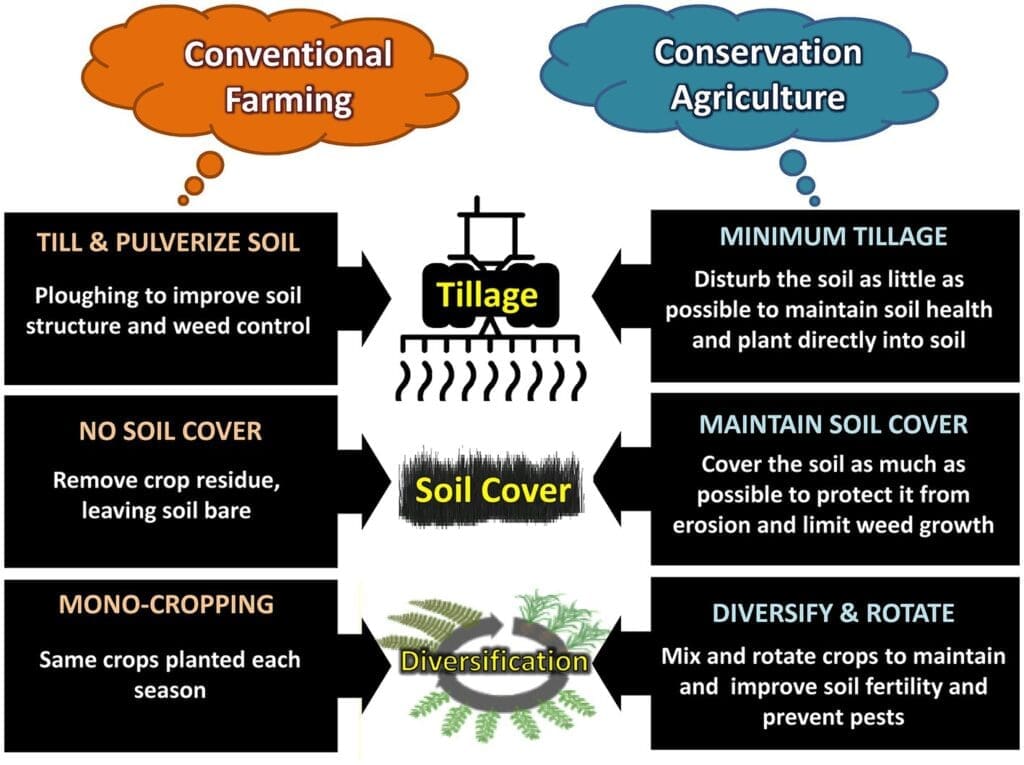
Rotating Crops to Maintain Soil Health
Crop rotation is an effective practice for both pest prevention and overall soil health maintenance. Planting different crops in different locations from season to season disrupts pest life cycles and reduces pest populations.
Furthermore, crop rotation helps maintain a well-balanced soil ecosystem. Different crops have varying nutrient requirements, and rotating them helps prevent nutrient depletion and reduce the build-up of pest populations that specifically target certain crops.
By implementing these soil health management practices, you can create a garden environment that is less attractive to pests and better equipped to prevent pest infestations.
Utilizing Organic Pest Control Methods
Organic pest control methods offer environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical pesticides and focus on utilizing nature’s own pest management systems. By embracing organic pest control, you can tackle pest infestations while preserving the overall health of your soil ecosystem.
Introduction to Organic Pest Control
Organic pest control involves using natural solutions to manage and prevent pest infestations. These methods prioritize biological control, physical barriers, and cultural practices to minimize the adverse impacts on the environment and human health.
Unlike chemical pesticides, organic pest control methods target specific pests while leaving beneficial insects unharmed. This approach promotes a balanced ecosystem where natural predators help control pest populations, reducing the reliance on chemical interventions.
Promoting Beneficial Soil Organisms for Pest Management
One of the key components of organic pest control is promoting beneficial soil organisms. These organisms, such as predatory insects, nematodes, and fungi, can help regulate pest populations naturally.
By creating a favorable habitat for beneficial organisms through soil health practices, you can encourage their establishment and enhance their effectiveness in controlling pests. Providing food sources, shelter, and appropriate moisture levels are vital for promoting beneficial soil organisms.
Using Companion Planting Techniques
Companion planting involves strategically planting certain plants together to maximize their benefits and deter pests. By interplanting pest-repellent plants or those that attract beneficial insects, you create an environment that confuses or repels pests while attracting natural predators.
For example, planting marigolds around vegetable beds can deter pests such as aphids and nematodes. On the other hand, growing herbs like cilantro and dill can attract beneficial insects that feed on pests.
Companion planting not only helps control pest populations naturally but also offers additional benefits such as improved pollination and soil fertility through nitrogen fixation.
By incorporating organic pest control methods into your pest management practices, you can effectively address pest infestations while preserving soil health and promoting a sustainable gardening environment.
Soil Health and Biological Pest Control
Maintaining a healthy soil ecosystem is essential for promoting biological pest control. By fostering soil biodiversity and understanding the role of soil microbes in pest control, you can harness natural mechanisms to keep pests in check.
Encouraging Soil Biodiversity for Pest Regulation
Soil biodiversity refers to the variety and abundance of organisms in the soil, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, nematodes, earthworms, and insects. A diverse soil ecosystem is crucial for pest regulation, as it promotes the presence of natural predators and creates an environment that is less favorable for pests.
Encouraging soil biodiversity can be achieved through practices such as minimizing disturbance, reducing the use of chemical inputs, and incorporating organic matter into the soil. By supporting a diverse range of soil organisms, you create a healthier and more resilient soil ecosystem that can naturally suppress pest populations.
Understanding the Role of Soil Microbes in Pest Control
Soil microbes, including bacteria and fungi, play a vital role in pest control. Some soil microbes have the ability to colonize plant roots and protect them against pests and diseases. These beneficial microbes form symbiotic relationships with plants, supplying them with essential nutrients and activating their defense mechanisms.
In addition to directly combating pests, soil microbes also contribute to overall soil health. They break down organic matter, release nutrients, improve soil structure, and enhance water-holding capacity. By actively promoting the presence and activity of beneficial soil microbes, you can effectively prevent and manage pest infestations.
By prioritizing soil health and fostering a diverse and thriving soil ecosystem, you can harness the power of biological pest control to minimize pest pressures and maintain a balanced garden environment.
Soil Health Practices for Specific Pest Prevention
Different pests require specific soil health strategies to prevent infestations effectively. By targeting the unique vulnerabilities of certain pests, you can implement tailored soil management practices to deter them.
Preventing Nematode Infestations through Soil Health Strategies
Nematodes are microscopic worm-like organisms that can cause significant damage to plant roots. Preventing nematode infestations requires creating unfavorable conditions for their survival and reproduction.
One effective strategy is solarization, which involves covering the soil with a transparent plastic sheet to harness the sun’s heat and raise the soil temperature. This process effectively kills nematodes and other soil pests. Additionally, incorporating organic matter rich in carbon can help reduce nematode populations, as it creates a less favorable habitat for their development.
Managing Soilborne Diseases through Soil Management
Soilborne diseases, caused by pathogens residing in the soil, can severely impact plant health. Proper soil management techniques can help prevent the spread and establishment of these diseases.
Maintaining good soil drainage and avoiding waterlogged conditions is essential, as many soilborne pathogens thrive in moist environments. Additionally, practicing crop rotation and incorporating disease-resistant varieties into your planting scheme helps break the disease cycle and reduces the risk of soilborne disease outbreaks.
Soil solarization, as mentioned earlier, can also be an effective method for managing soilborne diseases. By raising the soil temperature, solarization kills disease-causing pathogens and reduces their population in the soil.
Controlling Soil-Dwelling Pests with Healthy Soil Practices
Some pests reside in the soil and attack plant roots, causing significant damage. Implementing healthy soil practices can create an environment that discourages these soil-dwelling pests.
Improving soil structure and fertility through the addition of organic matter helps plants establish strong and healthy root systems, making them more resilient to soil-dwelling pests. Good soil drainage is crucial, as excessive moisture can create conditions that attract pests like wireworms and grubs.
Additionally, practicing crop rotation helps break pest life cycles and reduces the build-up of soil-dwelling pests in specific areas of your garden. By implementing these soil health practices, you can effectively control soil-dwelling pests and maintain the overall health of your garden.

Promoting Soil Health through Sustainable Practices
Choosing sustainable practices in managing soil health not only benefits plant growth but also contributes to a healthier environment. By utilizing organic fertilizers, cover crops, and reducing pesticide use, you can promote long-term soil health and prevent pest infestations.
Benefits of Organic Fertilizers for Soil Health
Organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources such as compost, manure, and plant-based materials, provide numerous benefits to soil health. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, organic fertilizers improve soil structure, enhance water retention, and promote the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms.
Incorporating organic fertilizers into your soil management practices not only provides essential nutrients to plants but also promotes long-term soil health. By maintaining optimal soil health, you can prevent nutrient imbalances, strengthen plant immunity, and discourage pest infestations.
Utilizing Cover Crops to Improve Soil Structure
Cover crops are non-commercial crops grown primarily to benefit the soil rather than for harvest. They are typically planted during fallow periods or between main crops and offer numerous advantages in improving soil health.
Cover crops help prevent soil erosion, reduce nutrient leaching, and improve soil structure by increasing organic matter content. They also create a favorable habitat for beneficial soil organisms, such as earthworms and beneficial bacteria, that naturally control pests.
By incorporating cover crops into your crop rotation plan, you can promote soil health, boost pest prevention, and achieve higher overall productivity in your garden.
Reducing Pesticide Use through Soil Health Improvement
Enhancing soil health minimizes the need for chemical pesticides by creating a natural defense system against pests. A healthy soil ecosystem with balanced nutrient levels, active beneficial organisms, and strong plant growth naturally deters pests.
Reducing pesticide use has several benefits, including promoting biodiversity, preventing environmental pollution, and preserving beneficial insects, such as bees and butterflies. By prioritizing soil health, you can practice sustainable pest management and reduce the reliance on chemical interventions.
By adopting sustainable practices such as utilizing organic fertilizers, incorporating cover crops, and reducing pesticide use, you can improve soil health, prevent pest infestations, and contribute to a more environmentally friendly gardening approach.
Long-Term Effects of Soil Health on Pest Management
Maintaining long-term soil health is vital for sustainable pest prevention and effective pest management. By considering the role of crop rotation and committing to consistent soil care practices, you can break pest cycles and ensure the resilience of your garden.
Role of Crop Rotation in Breaking Pest Cycles
Crop rotation is a proven practice for breaking pest cycles and minimizing pest infestations. By rotating crops each season, you disrupt the life cycles of pests that specifically target certain crops.
Some pests have a limited host range, meaning they rely on specific plants for survival and reproduction. By planting different crops in different areas of your garden, you make it difficult for pests to find suitable hosts, reducing their population and preventing infestations.
To maximize the benefits of crop rotation, it’s important to carefully plan your planting scheme, considering the pest vulnerabilities of different crops and their effect on soil health. By rotating crops effectively, you can manage pest pressures and maintain healthy soil conditions in the long term.
Maintaining Long-Term Soil Health for Sustainable Pest Prevention
Consistently nurturing soil health is crucial for sustainable pest prevention and long-term pest management success. By implementing soil care practices, such as incorporating organic matter, practicing crop rotation, and minimizing chemical inputs, you can maintain optimal soil conditions that discourage pests and support healthy plant growth.
A long-term commitment to soil health involves regular soil testing, monitoring changes in soil conditions over time, and adapting management practices accordingly. By addressing soil imbalances promptly and proactively, you can prevent pest infestations before they become significant issues.
By prioritizing the long-term health of your soil, you create an environment that promotes plant resilience, minimizes pest pressures, and establishes a sustainable approach to pest management.
Monitoring and Assessing Soil Health
Regular monitoring and assessment of soil health are essential for understanding the evolving conditions of your garden soil and identifying areas for improvement. By utilizing various methods for evaluating soil health and utilizing soil tests, you can make informed decisions to optimize soil conditions and prevent pest infestations.
Methods for Evaluating Soil Health
Several methods can be used to evaluate soil health. Physical observation and analysis can provide valuable insights into soil structure, texture, and compaction. Assessing soil moisture levels, water infiltration rates, and drainage patterns helps understand the drainage properties of the soil.
Additionally, assessing the presence and diversity of soil organisms, such as earthworms and beneficial insects, provides an indication of soil biological activity and overall soil health.
Utilizing Soil Tests to Improve Soil Conditions
Soil testing is a valuable tool in determining nutrient deficiencies, imbalances, and pH levels in the soil. Soil test results guide you in making informed decisions about appropriate fertilization and amendments needed to optimize soil conditions.
By regularly conducting soil tests, typically every two to three years, you can track changes in soil nutrient levels and adjust your soil management practices accordingly.
Monitoring Changes in Soil Health Over Time
Monitoring long-term changes in soil health is crucial for identifying trends and understanding the effectiveness of your soil management practices. Regular observations, record-keeping, and analysis of soil test results allow you to assess the impact of your efforts and make necessary adjustments.
By comparing soil health data over time, you can identify any deterioration or improvement in soil conditions and take corrective actions promptly. This iterative approach to soil health management ensures that you can prevent pest infestations and maintain optimal soil conditions for healthy plant growth.
Conclusion
Soil health plays a vital role in preventing and managing pest infestations. By understanding the impact of soil composition on pest populations, implementing effective soil management practices, utilizing organic pest control methods, and prioritizing long-term soil health, you can create an environment that discourages pests and supports healthy plant growth.
Maintaining healthy soil through proper soil amendments, drainage techniques, and crop rotation is a proactive approach to preventing pest infestations. By utilizing organic pest control methods, promoting soil biodiversity, and understanding the role of soil microbes in pest control, you can further enhance the natural pest management systems.
Additionally, adopting sustainable practices like using organic fertilizers, incorporating cover crops, and reducing pesticide use contributes to long-term soil health and pest prevention. Regular monitoring and assessment of soil health, along with utilizing soil tests, allow you to make informed decisions to optimize soil conditions and prevent pest infestations.
By prioritizing soil health and implementing these comprehensive strategies, you can effectively prevent and manage pest infestations while promoting a sustainable and healthy gardening environment.

I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.