Did you know that pests can have a significant impact on the agricultural industry? In the world of farming and crop production, pests can cause extensive damage to crops, resulting in expensive losses for farmers. Not only do pests directly harm the plants, but they can also indirectly affect the economy through increased costs for pest control measures and reduced crop yields. In this article, we will explore the economic impact of pests on agriculture and understand the importance of effective pest control solutions for sustainable farming practices. So, let’s delve into the fascinating world of pest control and its implications for the agricultural sector.
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive article on the economic impact of pests on agriculture. In this article, we will explore the definitions of pests and agriculture, and delve into the importance of agriculture for food production, economic growth, and employment. We will also discuss the various types of pests, their behavior, and the damage they can cause to crops. Furthermore, we will examine the economic impact of pests, including crop losses, the cost of pest management, price increases, and reduced agricultural productivity. To provide a global perspective, we will analyze the situation in both developing and developed countries. Additionally, we will explore effective pest control solutions, such as integrated pest management, biological control, and chemical control, and discuss the benefits of implementing these solutions, including increased crop yield, cost savings, and environmental sustainability. Lastly, we will present case studies highlighting the impact of pest outbreaks and successful pest control strategies. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of the economic impact of pests on agriculture and the importance of effective pest control measures.
1. Definitions
1.1 Pest
A pest refers to any organism that poses a threat or nuisance to crops, livestock, or humans. These organisms can include insects, rodents, fungi, weeds, and microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses. Pests can cause significant damage to agricultural production and are a constant challenge for farmers and agricultural industries worldwide.
1.2 Agriculture
Agriculture is the practice of cultivating plants and raising animals for food, fiber, medicinal plants, and other products used to sustain human life. It encompasses various activities, including crop production, livestock farming, aquaculture, and forestry. Agriculture is vital for food security, providing raw materials for industries, and supporting rural livelihoods.

2. Importance of Agriculture
2.1 Food Production
Agriculture plays a critical role in producing the food necessary to sustain the world’s growing population. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately 80% of the world’s food supply is derived from crops and livestock. Without efficient and productive agricultural practices, global food security would be at risk.
2.2 Economic Growth
Agriculture contributes significantly to the economic growth of nations, particularly in developing countries where it is often the primary source of income for rural communities. In addition to generating employment opportunities, agriculture drives the growth of related industries such as manufacturing, food processing, and agribusiness. The sector’s contribution to GDP varies across countries but is consistently substantial.
2.3 Employment
Agriculture is a significant source of employment globally, providing livelihoods for millions of people. Small-scale farmers, farm laborers, and individuals involved in the agricultural value chain contribute to rural economies and help alleviate poverty. Furthermore, agriculture offers opportunities for entrepreneurship and the development of rural enterprises.
3. Understanding Pests
3.1 Types of Pests
Pests in agriculture encompass a wide range of organisms that can harm crops, livestock, and agricultural infrastructure. Insects, such as aphids, beetles, and caterpillars, are common crop pests that feed on plants and cause yield losses. rodents, such as rats and mice, can damage crops and contaminate stored produce. Weeds compete with crops for resources, leading to reduced yields. Fungal pathogens can infect plants and cause diseases that affect overall crop health and productivity. Understanding the different types of pests is crucial for implementing targeted control measures.
3.2 Pest Behavior
To effectively manage pests, it is essential to understand their behavior. Pests have distinct life cycles, feeding habits, reproductive patterns, and preferences for specific crops or environmental conditions. For example, some insects lay eggs on or near leaves, while others bore into the stems or fruits of plants. By studying pest behavior, farmers and pest control professionals can devise strategies to disrupt their life cycles and prevent infestations.
3.3 Pest Damage
Pest damage can have severe consequences for agricultural production. Insects and rodents can devour or destroy crops, leading to reduced yields and financial losses for farmers. Weeds can compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight, resulting in stunted growth and decreased productivity. Fungal diseases can cause wilting, rotting, and discoloration in plants, further compromising overall crop health. By understanding the extent and types of damage pests can cause, farmers can take proactive measures to mitigate losses.

4. Economic Impact
4.1 Crop Losses
Pests are a significant cause of crop losses globally. According to the FAO, pests are estimated to destroy around 20-40% of global crop production annually. These losses not only affect food availability but also result in financial hardship for farmers. Crop losses can vary depending on the type of pest, crop, and region, but the overall impact is substantial.
4.2 Cost of Pest Management
Managing pests in agriculture involves implementing various strategies, including pest surveys, monitoring, prevention, and control measures. The cost of pest management can be significant, as it encompasses expenses related to labor, materials, equipment, and pest control products. Additionally, farmers may need to invest in training and education to stay updated on the latest pest control techniques and regulations.
4.3 Price Increase
The economic impact of pests extends beyond the agricultural sector. When crop losses occur due to pest damage, the reduced supply of certain crops can lead to a price increase in the market. This price increase affects consumers, especially those in low-income communities who may already struggle to afford nutritious food. Additionally, rising food prices can have detrimental effects on national economies and contribute to inflation.
4.4 Reduced Agricultural Productivity
Pest infestations and crop losses ultimately result in reduced agricultural productivity. When farmers are unable to produce crops to their full potential, their incomes decline, and overall agricultural output decreases. Diminished agricultural productivity can have a cascading effect on employment, rural development, and food security. Consequently, addressing the economic impact of pests becomes crucial for sustainable agricultural practices and national economies.
5. Global Scenario
5.1 Developing Countries
Pests have a disproportionate impact on agriculture in developing countries. These nations often face resource constraints, inadequate infrastructure, and limited access to modern pest control technologies. Consequently, crop losses due to pests can be devastating, exacerbating food insecurity and poverty. Addressing the economic impact of pests in developing countries requires targeted interventions, knowledge sharing, and investments in capacity building.
5.2 Developed Countries
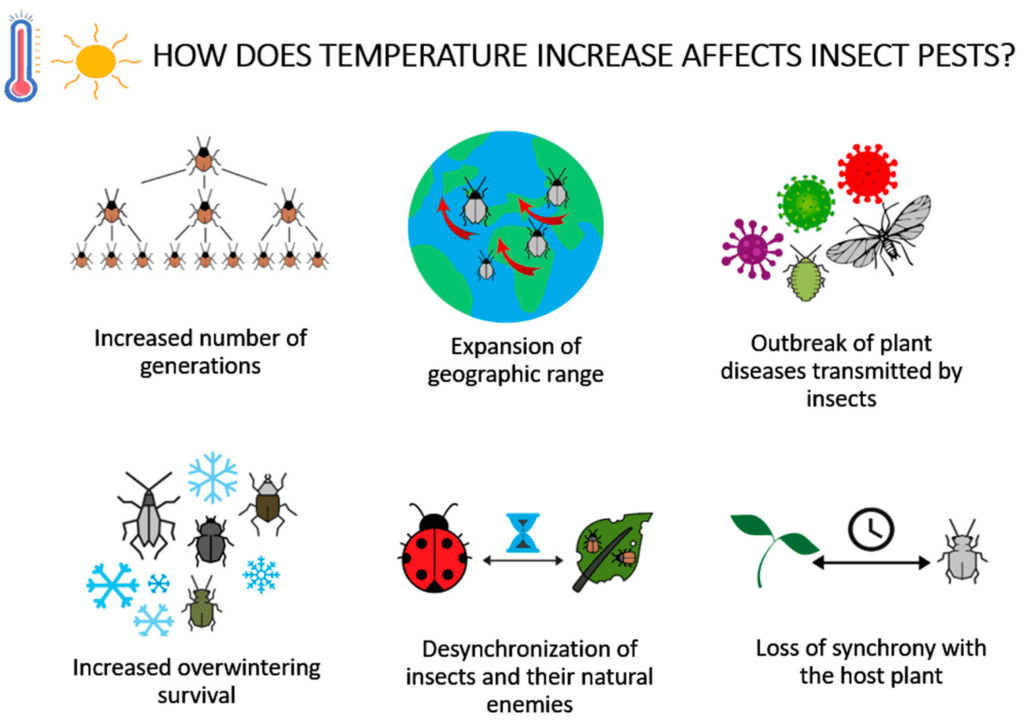
Even in developed countries with advanced agricultural systems, pests continue to pose economic challenges. While these countries may have access to advanced pest control technologies and resources, the complexity of pest management remains a constant concern. Invasive pests, climate change, and evolving pesticide resistance are some of the issues faced by developed countries. Sustainable and integrated pest management practices are crucial for minimizing economic losses and ensuring resilient agricultural systems.
6. Pest Control Solutions
6.1 Integrated Pest Management
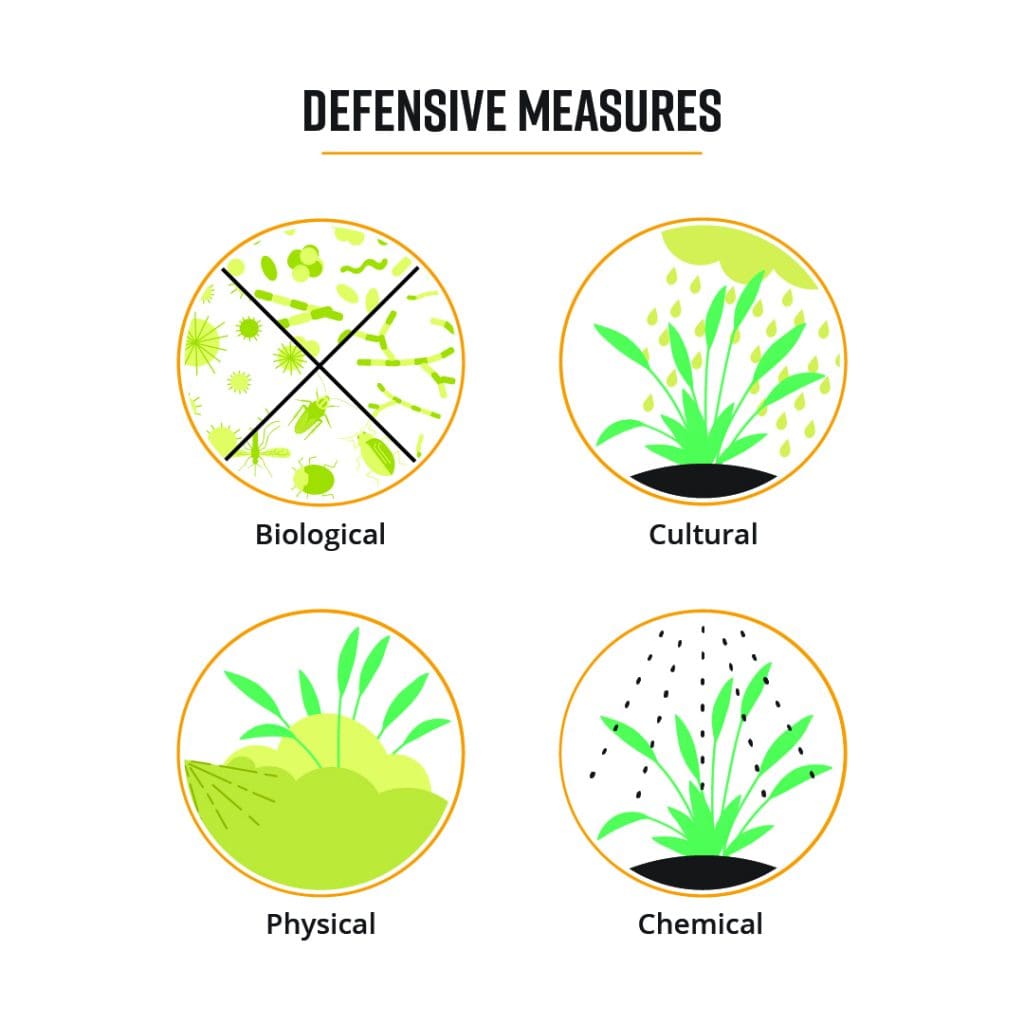
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an approach that combines various pest control techniques to manage pests effectively while minimizing environmental and economic impacts. IPM involves thorough monitoring and identification of pests, implementing preventive measures, utilizing biological control agents, and judicious use of pesticides only when necessary. The integration of multiple strategies helps reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and promotes sustainable pest management practices.
6.2 Biological Control
Biological control involves using natural enemies, such as predators, parasitoids, and pathogens, to control pest populations. These natural enemies prey upon or parasitize pests, helping to keep their populations in check. Biological control is a sustainable and environmentally friendly pest management strategy that has gained popularity due to its effectiveness and reduced reliance on chemical pesticides.
6.3 Chemical Control
Chemical control, in the form of pesticides, is another tool in pest management. Chemical pesticides can be effective in controlling pests, but their use must be judicious to minimize negative impacts on human health and the environment. Integrated Pest Management often emphasizes using pesticides as a last resort and employing them in a targeted manner to reduce collateral damage to beneficial organisms.
7. Benefits of Effective Pest Control
7.1 Increased Crop Yield
Implementing effective pest control measures can lead to increased crop yield. By managing pests and preventing significant damage to crops, farmers can maximize their production potential. Healthy and pest-free crops are more likely to mature properly, produce higher yields, and contribute to food security.
7.2 Cost Savings
Effective pest control can result in cost savings for farmers. By preventing or minimizing pest damage, farmers can avoid financial losses associated with crop losses and the cost of pest management. Additionally, utilizing sustainable pest control practices, such as biological control, can reduce the need for expensive chemical pesticides, further reducing costs.
7.3 Environmental Sustainability
Implementing sustainable pest control practices, such as Integrated Pest Management and biological control, contributes to environmental sustainability. By reducing reliance on chemical pesticides, the release of harmful pollutants into the environment can be minimized. Furthermore, biological control and other environmentally friendly techniques help preserve biodiversity and promote ecosystem health.
8. Case Studies
8.1 Impact of Pest Outbreaks
Pest outbreaks can have devastating consequences on a large scale. One notable case is the impact of the desert locust, a notorious pest that poses a significant threat to agriculture across continents. Desert locust swarms can devastate crops, resulting in food scarcity and economic losses. Countries in East Africa, such as Ethiopia, Kenya, and Somalia, have experienced severe outbreaks in recent years, leading to the destruction of crops and threatening food security.
8.2 Successful Pest Control Strategies
Various case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of pest control strategies. For instance, the successful implementation of Integrated Pest Management in rice production in Southeast Asia has led to significant yield improvements and reduced reliance on chemical pesticides. In Ghana, the application of biological control methods, such as the release of natural enemies, has helped mitigate the impact of cocoa pests and improve cocoa bean quality. These success stories highlight the importance of implementing appropriate pest control measures tailored to specific crops and regions.
10. Conclusion
The economic impact of pests on agriculture is undeniable. Pests can cause significant crop losses, increase the cost of pest management, result in price increases, and reduce agricultural productivity. However, by understanding pests, implementing effective pest control measures, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices, we can mitigate these economic impacts. Integrated Pest Management, biological control, and targeted chemical control offer viable solutions to manage pests efficiently and minimize negative consequences. The benefits of effective pest control include increased crop yield, cost savings, and environmental sustainability. Furthermore, successful case studies showcase the importance of addressing pest outbreaks promptly and implementing tailored pest control strategies. By prioritizing the economic impact of pests on agriculture, we can ensure food security, promote economic growth, and create sustainable agricultural systems for the future.

I am Randy, the author behind PestControld.com. Drawing from decades of experience, I aim to provide valuable insights, expert advice, and practical recommendations to help you make informed decisions when assessing viable pest control solutions.